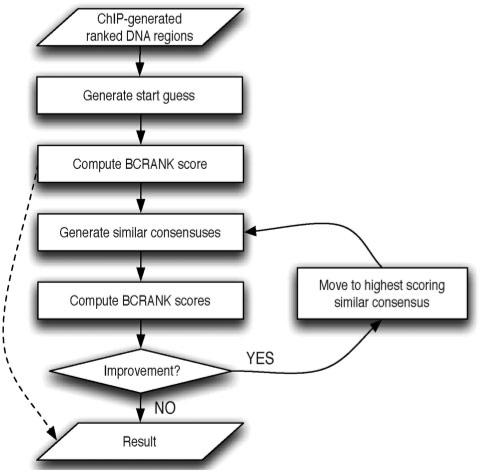
Figure 1.
Overview of the BCRANK algorithm. A file containing DNA sequences, ranked by ChIP-enrichment, is given as input. Then a consensus sequence is generated, either at random or by manual selection, and its BCRANK score is computed. Optionally, BCRANK can be used to assign scores to previously known consensus sequences, and in such case the algorithm stops here, indicated by dotted line in the figure. Otherwise the algorithm will continue to optimize the consensus by constantly moving to a similar consensus with a higher BCRANK score until no further improvement is possible and a locally optimal solution is reported. The chance of finding the globally optimal solution can be increased by re-starting BCRANK several times with different random start guesses.