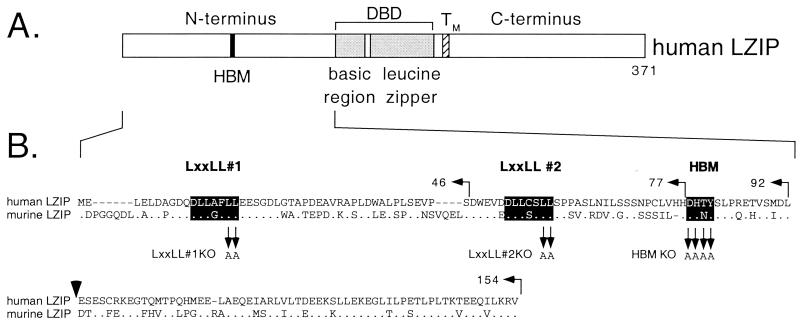
Figure 1.
(A) Structure of human LZIP. The bZIP DNA-binding and dimerization domain, composed of a basic region (residues 152–171) and adjacent leucine zipper (residues 178–220), lies near the center of the polypeptide (shaded) and is flanked by a putative transmembrane domain (TM, residues 229–243; ref. 35). The HBM (filled box) is located in the N terminus (DHTY, residues 78–81). The N terminus is rich in bulky hydrophobic residues (especially leucine) and contains two clusters of acidic residues (residues 16–52, 30% acidic; residues 93–148, 27% acidic). The C terminus is also rich in bulky hydrophobic amino acids as well as prolines. (B) Alignment of the N-terminal sequences of human and mouse LZIP (15–17). The two LxxLL motifs and the HBM (highlighted) represent islands of greatest sequence conservation. The endpoints of truncations used in this study are indicated above the sequence, and residues targeted for alanine substitution are indicated below the alignment. A vertical arrowhead marks the insertion point of a mRNA-splice variant that adds an extra 15 amino acids (17).