Fig. 1.
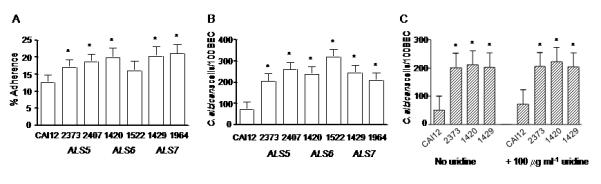
Adhesion assay data. Histogram showing the adherence of C. albicans strains to monolayers of human umbilical vascular endothelial cells (A), and buccal epithelial cells (B and C). Asterisks mark results that are significantly different from the control strain CAI12 (P < 0.05). Deletion of ALS5, ALS6 or ALS7 results in increased adhesion of C. albicans yeast forms to both cell types. Reintegration of a wild-type allele complemented the als6Δ/als6Δ strain in the endothelial cell assay. In general, however, reintegration of a single ALS allele did not complement the mutant phenotype suggesting the potential for allelic effects or a gene dosage requirement for full activity. Increased adhesive effects were also observed for C. albicans yeast forms cultured in the presence of excess uridine (C), suggesting that the results observed in (A) and (B) are not due to placement of the URA3 marker.
