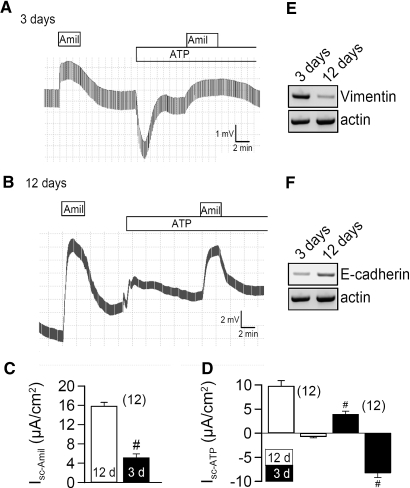
Figure 1.
Ion conductances in M1 cells are determined by cell polarization. Original recordings of transepithelial voltages and effects of luminal amiloride (Amil, 10 μM) and ATP (10 μM) measured in little polarized (A) and highly polarized (B) M1 monolayers. (C) Summary of the equivalent amiloride sensitive short circuit currents (Isc) in M1 cells grown to low (3 d; black bars) or high (12 d; white bars) polarization. (D) Summary of ATP-activated short circuit currents (Isc after ATP-stimulation − Isc under control conditions = ΔIsc or Isc -ATP). In poorly polarized monolayers, ATP activates a Cl- secretion (negative voltage deflection), while highly polarized cells activate a K+ secretion (positive voltage deflection). # indicates significant difference between M1 cells at low and high polarization (unpaired t test). n = number of monolayers. (E) The EMT marker vimentin is expressed at higher levels in poorly polarized cells (RT-PCR; n = 2). (F) Higher levels of E-cadherin are found in differentiated cells (RT-PCR; n = 2).