Figure 1. Flexibility of neurofilaments.
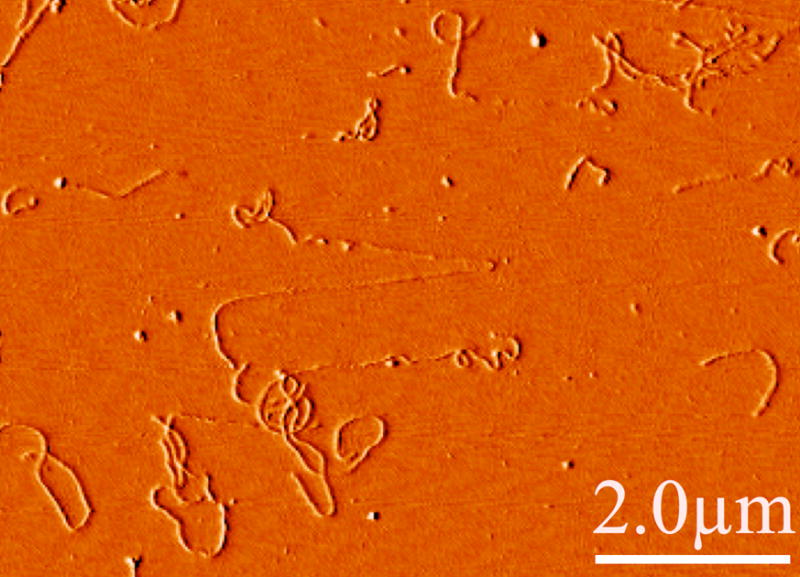
Atomic force micrograph showing a typical image of hydrated, native bovine spinal cord neurofilaments deposited from solution on a mica surface to which they strongly adhere. Note the significant flexibility on a length scale less than a micron. Occasionally, stretched filaments such as that shown in the center with apparently smaller diameters are seen, possibly as the result of flow-induced forces as the filaments adhered or as the AFM cantilever moved laterally across the surface.
