Figure 8.
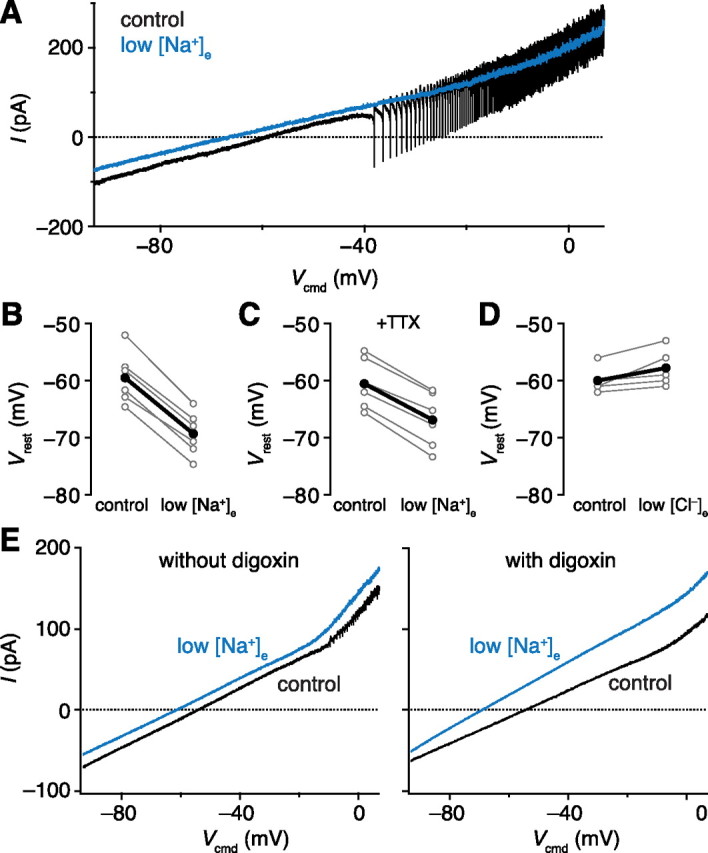
A sodium conductance depolarizes the resting membrane potential of projection neurons. A, Current–voltage relationships measured by a slow voltage ramp command. Single sweeps are shown. B, Resting potentials in control and low [Na+]e (p = 1.25 × 10−5, paired t test). Individual cells are in gray and averages are in black for B–D. C, Resting potentials in control and low [Na+]e in the presence of TTX (p = 2.13 × 10−5, paired t test). The hyperpolarization caused by low [Na+]e is significantly smaller in TTX [p = 8.21 × 10−4, difference = (−5.07, −1.87) mV, unpaired t test]. D, Resting potentials in control and low [Cl−]e (p = 0.0514, paired t test). E, Average current–voltage relationships (n = 6 sweeps) recorded from a representative PN in control and low [Na+]e with and without digoxin. Low [Na+]e caused a statistically significant hyperpolarization in digoxin (n = 5, p = 8.82 × 10−4, paired t test).
