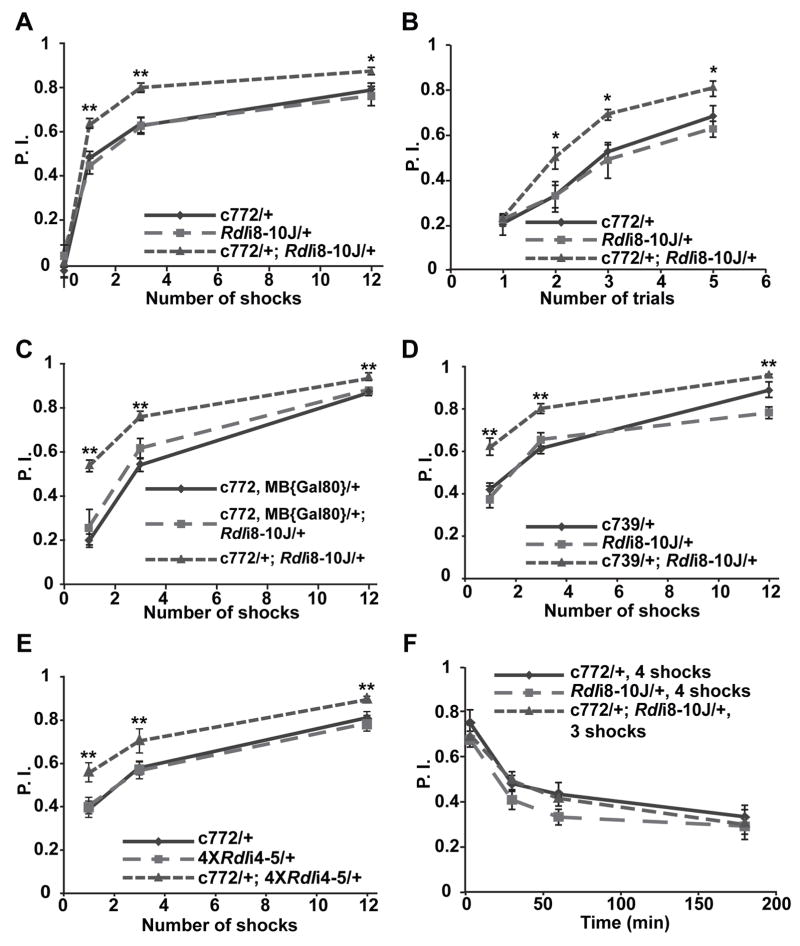
Figure 6. Enhanced olfactory learning with Rdl knock-down in the MBs.
(A) The Rdl knock-down flies carrying the c772-Gal4 driver and the UAS-RdlRNAi construct Rdli8-10J exhibited enhanced olfactory learning using 1, 3 or 12 electric shock pulses presented within a 1 min exposure to the conditioned odor.
(B) Flies carrying the c772-Gal4 driver and the UAS-RdlRNAi construct Rdli8-10J exhibited a similar enhancement of olfactory learning after multiple trials consisting of a 10 sec odor presentation along with a single electric shock pulse.
(C) Knock-down of Rdl by the combined c772-Gal4,MB{Gal80} driver did not affect acquisition while knock-down by the original c772-Gal4 driver enhanced acquisition.
(D) The Rdl knock-down flies carrying the c739-Gal4 driver and the UAS-RdlRNAi construct Rdli8-10J exhibited enhanced olfactory learning using 1, 3 or 12 electric shock pulses presented within a 1 min exposure to the conditioned odor.
(E) The Rdl knock-down flies carrying the c772-Gal4 driver and the UAS-RdlRNAi constructs 4XRdli4-5 show enhanced olfactory learning using 1, 3 or 12 shock pulses presented within a 1 min odor exposure.
(F) The Rdl knock-down flies exhibited normal memory decay. The Rdl knock-down flies and the two control groups were trained to a similar initial performance level by using a different number of electric shock pulses along with a 1 min presentation of the conditioned odor. There was no significant difference in performance among the three groups at any of the time points tested. For all panels, n = 6 for each group. Means ± SEM are shown. *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01.