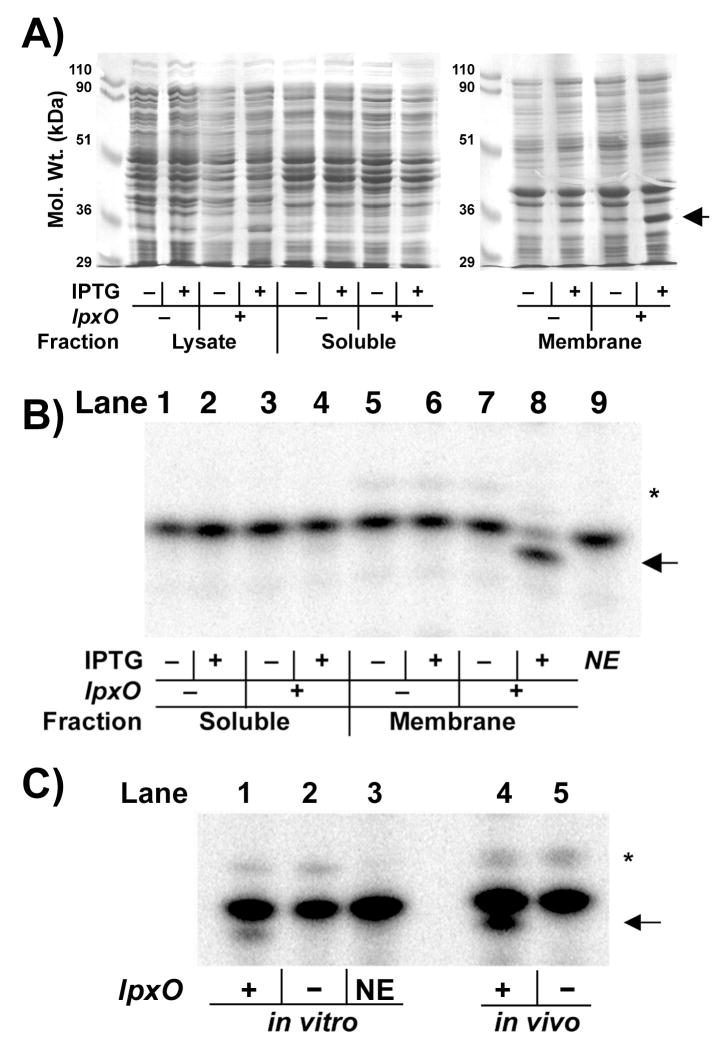
Figure 4. Over-expression and catalytic activity of membrane-associated LpxO.
A) Coomassie-blue stained SDS-gel of sub-cellular fractions from LpxO-over-expressing E. coli. The LpxO protein (arrow) migrates as a 35-kDa protein and is localized in the membrane fraction. B) Incubation of E. coli Kdo2-[4′-32P]-lipid A in the LpxO assay system, described in the Materials and Methods, with 0.1 mg/ml cytosol (lanes 1–4) or 0.1 mg/ml membranes (lanes 5–8) of E. coli BLR(DE3)/pLysS harboring pET21a+ (lanes 1, 2, 5, 6) or pHSG2 (lanes 3, 4, 7, 8) for 60 min. Lipid A species were separated by TLC in CHCl3/pyridine/formic acid/H2O (50:50:16:5, v/v) after mild acid hydrolysis of the reaction product at pH 4.5 to remove the Kdo disaccharide (75). The hydroxylated lipid A product is highlighted by the arrow. NE indicates (lane 9) the no-enzyme control. C) Chromatographic comparison of lipid A 1,4′-bis-phosphate species generated in vitro by LpxO-over-expressing membranes (lane 1) at 0.01 mg/ml for 5 min to matched vector or no-enzyme controls (lanes 2 and 3), and to the lipid A species obtained from 32Pi-labeled wild-type (lane 4) or lpxO::kan mutant S. typhimurium (lane 5). The asterisk indicates the hepta-acylated product formed by the outer membrane enzyme PagP (17).