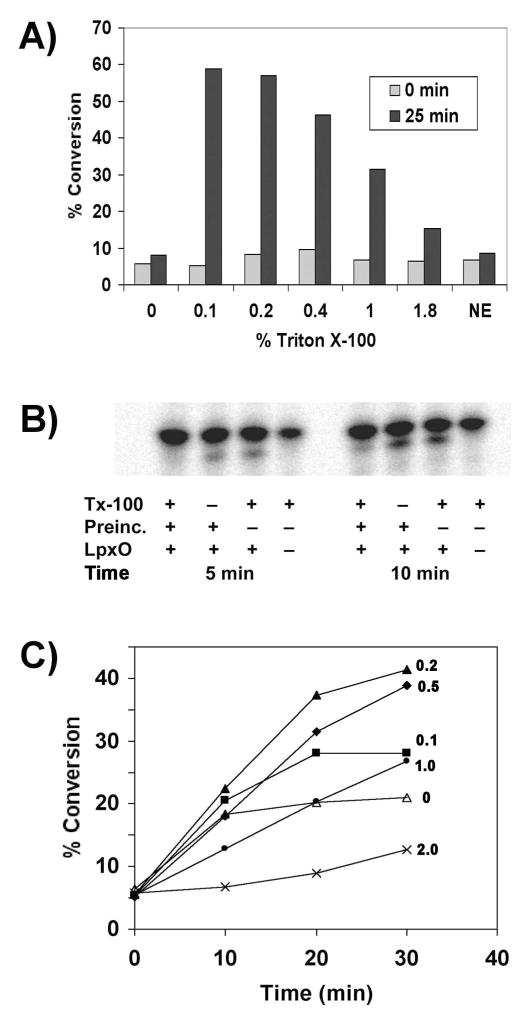
Figure 7. Detergent and phospholipid dependence of LpxO activity.
A) LpxO-catalyzed conversion of Kdo2-lipid A to its hydroxylated derivative was monitored after 25 min in the presence of increasing amounts of Triton X-100 (% v/v) at 0.1 mg/ml membrane protein. NE, no-enzyme control. B) Inactivation of LpxO by pre-incubation for 30 min at 0.02 mg/ml membrane protein in assay buffer containing Triton X-100 prior to initiation of the reaction by addition of the full set of cofactors and substrates to give a final membrane protein concentration of 0.01 mg/ml. C) Addition of E. coli phospholipids to the LpxO assay cocktail partially stabilizes LpxO activity, when assayed at 0.01 mg/ml membrane protein. Time courses of product formation (without pre-incubation) were followed for assay mixtures supplemented with 0 (open triangles), 0.1 (closed squares), 0.2 (closed triangles), 0.5 (closed diamonds), 1.0 (closed circles), or 2 mg/ml (x x) of exogenous E. coli phospholipids (as indicated by the numbers on the graph). The rate and extent of product formation with time were deemed optimal with 0.2 or 0.5 mg/ml phospholipids.