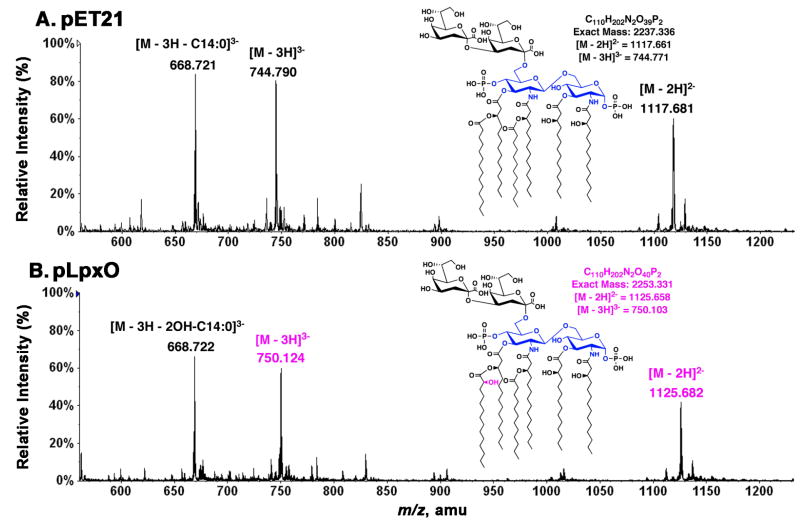
Figure 8. ESI/MS analysis of the LpxO reaction product.
Negative-ion mode ESI/MS spectra were acquired for re-purified Kdo2-lipid A samples that had been incubated in vitro for 2 h under assay standard conditions with 0.1 mg/ml membranes from either the vector control strain harboring pET21a+ (A) or from the LpxO-over-expressing strain harboring pHSG2 (B). The [M-2H]2− ions at m/z 1117.681 and at m/z 1125.682 correspond to the substrate (Kdo2-lipid A) and its hydroxylated product, respectively. The [M-3H]3− ions of these two species (at m/z 744.790 and m/z 750.124 respectively) are also very prominent, as noted previously (38). The triply charged ions near m/z 688.72, seen in both samples, arise by neutral loss of the 3′-secondary acyl chain from the triply charged Kdo2-lipid A ions. The extensive neutral loss from the triply charged ions is likely due to the fact that the triply charged ions undergo more energetic collisional activation in the ion source region during ESI/MS than do the doubly charged ions (38). This unusual property of Kdo2-lipid A (and its hydroxylated derivative) confirms that the LpxO-dependent hydroxylation of Kdo2-lipid A occurs exclusively on the 3′-secondary acyl chain in vitro, as it does in vivo.