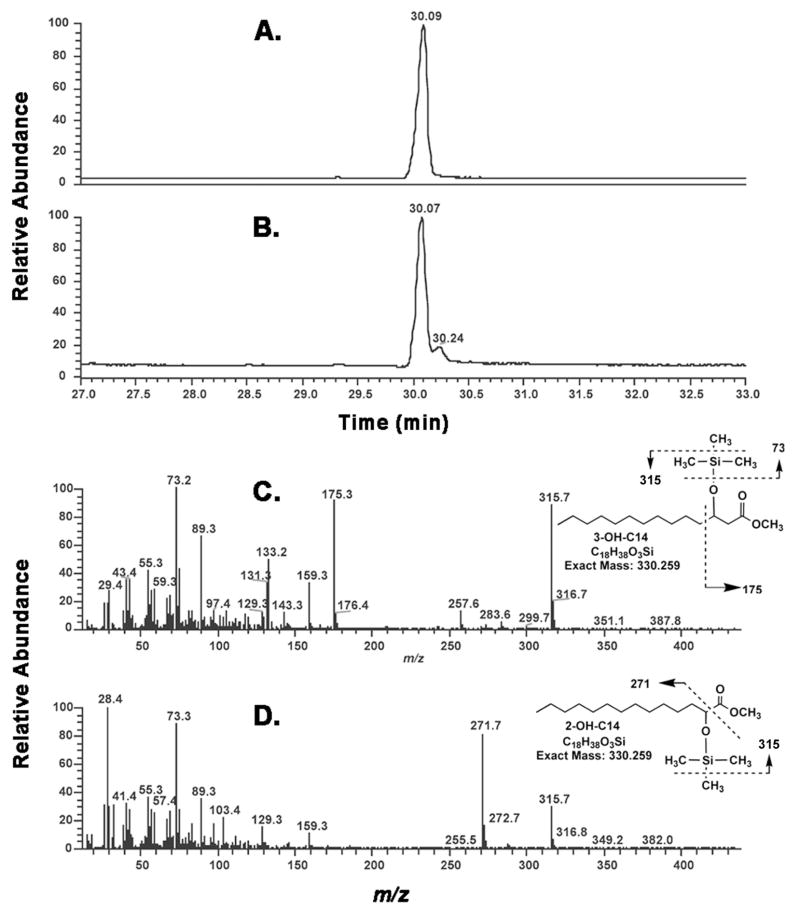
Figure 9. GC/MS analysis of the hydroxylated fatty acids in the vitro product generated by LpxO.
Kdo2-lipid A was incubated with vector control or LpxO membranes, as described in the Materials and Methods. The Kdo2-lipid A or the hydroxylated product formed by LpxO were re-isolated as a mixture from the reaction system, hydrolyzed, and converted to TMS derivatives to generate the fatty acid methylesters. Panel A. Total ion chromatogram (TIC) of the GC/MS analysis of the hydroxy fatty acids from the vector control reaction, showing the presence of a single peak consistent with a TMS-3-hydroxymyristoylmethylester. Panel B. TIC of the GC/MS analysis of the hydroxy fatty acids from the LpxO reaction system, showing the presence a shoulder peak with the expected retention time for a TMS-2-hydroxymyristoylmethylester. The peak area ratio between the TMS-3-hydroxymyristoylmethylester and the TMS-2-hydroxymyristoylmethylester is about 5 to 1. Panel C. EI/MS spectrum of the major leading peak in panel B (retention time: 30.07 min), showing identity with a TMS-3-hydroxymyristoylmethylester standard (see Supporting Information Fig. S1). Panel D. EI/MS spectrum of the minor lagging peak in panel B (retention time: 30.24 min), showing identity with a TMS-2-hydroxymyristoylmethylester standard (see Supporting Information Fig. S1). The proposed origins of the major fragments are indicated.