Figure 1.
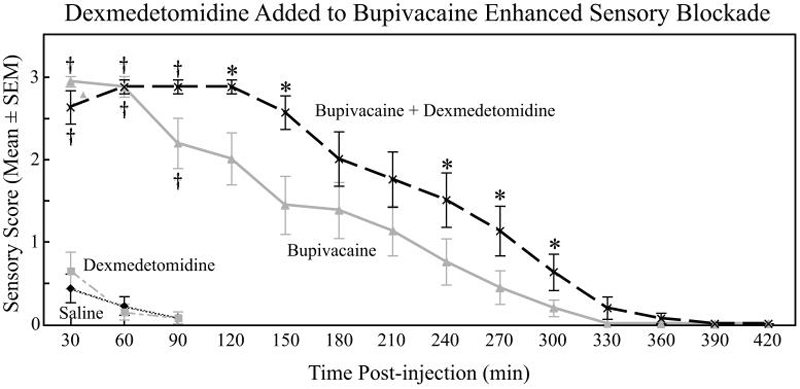
Sensory blockade- Dexmedetomidine added to bupivacaine enhanced the duration of sensory blockade in response to lateral paw pinch when compared with bupivacaine alone. Bupivacaine and bupivacaine plus dexmedetomidine showed improved sensory scores when compared with saline and dexmedetomidine. The time course demonstrates the progression from complete sensory blockade (score = 3) to recovery of normal sensory function (score = 0). Time course data for sensory testing were analyzed using a non-parametric model with ordinal logistic regression for repeated measures and generalized estimating equations. Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences for bupivacaine plus dexmedetomidine versus bupivacaine alone at specific times post-injection. † indicates significant differences between dexmedetomidine and saline when compared with bupivacaine plus dexmedetomidine and bupivacaine.
