Abstract
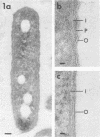
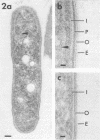
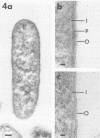
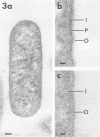
Clinical isolates of Legionella pneumophila, L. micdadei, L. bozemanii, and L. dumoffii were grown on charcoal-yeast extract agar from a living-medium inoculum and prepared for transmission electron microscopy by three different methods. Cells of all four Legionella species possessed cytoplasmic vacuoles, a gram-negative type of cell envelope with a dense peptidoglycan-like layer, a ruthenium red-positive polysaccharide capsule, and a single subpolar flagellum. The dense polysaccharide capsule seen on cells of L. micdadei was separated from the outer membrane by an extra layer of electron-lucent material that was not present on cells of the other species examined.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bozeman F. M., Humphries J. W., Campbell J. M. A new group of rickettsia-like agents recovered from guinea pigs. Acta Virol. 1968 Jan;12(1):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cagle G. D. Fine structure and distribution of extracellular polymer surrounding selected aerobic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Mar;21(3):395–408. doi: 10.1139/m75-055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler F. W., Cole R. M., Hicklin M. D., Blackmon J. A., Callaway C. S. Ultrastructure of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. A study using transmission electron microscopy. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):642–647. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Geesey G. G., Cheng K. J. How bacteria stick. Sci Am. 1978 Jan;238(1):86–95. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0178-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN J. A., SPURLOCK B. O. A new epoxy embedment for electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1962 Jun;13:437–443. doi: 10.1083/jcb.13.3.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Gorman G. W., Langford N. C., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B. Charcoal-yeast extract agar: primary isolation medium for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.437-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesher A. R., Ito S., Mansheim B. J., Kasper D. L. The cell envelope of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Morphologic and biochemical characteristics. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):628–630. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. Nature of the determinant responsible for the adhesion of lactobacilli to chicken crop epithelial cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Apr;87(2):245–250. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-2-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glavin F. L., Winn W. C., Jr, Craighead J. E. Ultrastructure of lung in Legionnaires' disease. Observations of three biopsies done during the Vermont epidemic. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):555–559. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gress F. M., Myerowitz R. L., Pasculle A. W., Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Dowling J. N. The ultrastructural morphologic features of Pittsburgh pneumonia agent. Am J Pathol. 1980 Oct;101(1):63–77. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant G. O., Lambert M. S., Moss C. W. Identification of diaminopimelic acid in the Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):815–818. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.815-818.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Moss C. W., McDougal L. K., Bozeman F. M., McKinney R. M., Brenner D. J. The rickettsia-like organisms TATLOCK (1943) and HEBA (1959): bacteria phenotypically similar to but genetically distinct from Legionella pneumophila and the WIGA bacterium. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jan;92(1):45–52. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keel J. A., Finnerty W. R., Feeley J. C. Fine structure of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. In-vitro and in-vivo studies of four isolates. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):652–655. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewallen K. R., McKinney R. M., Brenner D. J., Moss C. W., Dail D. H., Thomason B. M., Bright R. A. A newly identified bacterium phenotypically resembling, but genetically distinct from, Legionella pneumophila: an isolate in a case of pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Dec;91(6):831–834. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-6-831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):347–368. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade J. E., Brenner D. J., Bozeman F. M. Legionnaires' disease bacterium isolated in 1947. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):659–661. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Myerowitz R. L., Rinaldo C. R., Jr New bacterial agent of pneumonia isolated from renal-transplant recipients. Lancet. 1979 Jul 14;2(8133):58–61. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90117-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers F. G., Davey M. R. Ultrastructure of the cell envelope layers and surface details of Legionella pneumophila. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Jul;128(7):1547–1557. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-7-1547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers F. G., Greaves P. W., Macrae A. D., Lewis M. J. Electron microscopic evidence of flagella and pili on Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Dec;33(12):1184–1188. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.12.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers F. G. Ultrastructure of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Dec;32(12):1195–1202. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.12.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer E. L., Roth I. L. The ultrastructure of the capsules of Diplococcus pneumoniae and Klebsiella pneumoniae stained with ruthenium red. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):21–31. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr, Myerowitz R. L. The pathology of the Legionella pneumonias. A review of 74 cases and the literature. Hum Pathol. 1981 May;12(5):401–422. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(81)80021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]