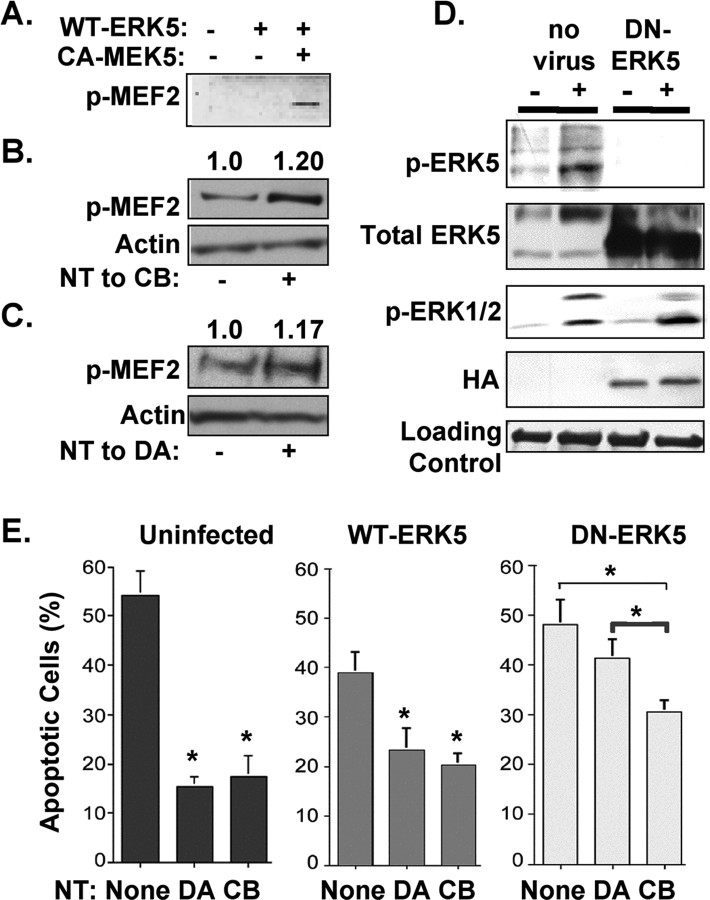
Figure 3.
ERK5 regulates MEF2D and promotes survival in response to target derived neurotrophins. A, MEF2D is phosphorylated in response to ERK5 activation. COS cells were transfected with CA–MEK5 and WT–ERK5, or WT–ERK5 alone, and lysates were blotted with an antibody to phospho-MEF2 (p-MEF2). B, MEF2D is phosphorylated in response to cell body stimulation (20 ± 8% increase, p < 0.05) for 20 min. Lysates were blotted with an antibody to phospho-MEF2 and with an antibody to pan-actin as a loading control. C, MEF2D is phosphorylated in response to distal axon stimulation (17 ± 6% increase, p < 0.05) for 2 h. Lysates were blotted with an antibody to phospho-MEF2 and with an antibody to pan-actin as a loading control. D, Neurons were infected with an adenovirus that expresses HA-tagged ERK5-dominant negative form (DN–ERK5), then treated with neurotrophins for 30 min. Compared with uninfected neurons, expression of DN–ERK5 prevents ERK5 phosphorylation without inhibiting ERK1/2 activation. E, ERK5 supports neuronal survival induced by target-derived neurotrophins. Cell apoptosis was measured by TUNEL staining in uninfected neurons and in neurons infected with WT–ERK5 or DN–ERK5 for 2 d. DN–ERK5 blocks survival of neurons that depend on target-derived neurotrophins, whereas DN–ERK5 has a lesser effect on survival supported by cell body stimulation. All data shown are means ± SEM, *p ≤ 0.05.