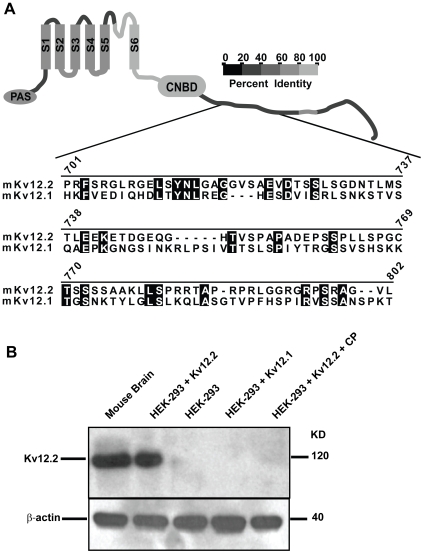
Figure 3. Characterization of the Kv12.2 channel antibody.
(A) Alignment of a 100 amino acid section, 702–801 of the cytoplasmic C-terminus of mouse Kv12.2 used to generate a Kv12.2-specific polyclonal antibody in rabbit to Kv12.1. The homologous region of Kv12.3 (not shown), is most similar to Kv12.1. Amino acid identities are shaded and numbers indicate amino acid position in Kv12.2. The cartoon depicts a Kv12.2 subunit with 6 transmembrane domains (S1–S6), a Per-Arnt-Sim (PAS) motif and a putative cyclic nucleotide binding motif (cNBD). Gray scale coding indicates the level of amino acid identity shared between Kv12.2 and other Kv12 channels in each region of the channel. (B) Top panel, Western blot analysis demonstrates that the Kv12.2 antibody (anti-Kv12.2) recognizes a single band of ∼120 KD (the predicted size of a Kv12.2 channel monomer) from mouse brain and HEK-293 cells transiently transfected with mKv12.2 channel cDNA (HEK-293+Kv12.2). Anti-Kv12.2 did not recognize specific bands in non-transfected HEK-293 cell lysates (HEK-293), in HEK-293 cells transfected with the closely related Kv12.1 channel (HEK-293+Kv12.1), or when excess antigenic control peptide (CP) was present to block immunodetection (HEK-293+Kv12.2+CP). Bottom panel, anti-β-actin demonstrates equal protein loading for each condition. These experiments were repeated 4 times yielding similar results.