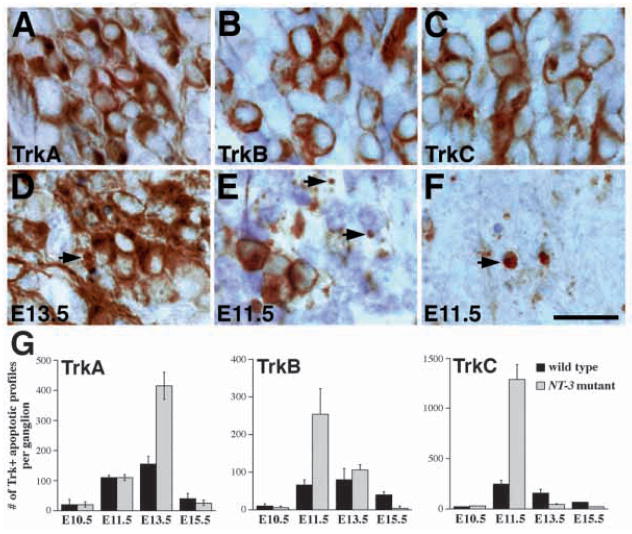
Fig. 7.
Stage-dependent apoptotic cell death of TrkA-, TrkB- and TrkC-expressing neurons in NT-3 mutant embryos. (A,D) RTA immunoreactivity in wild-type (A) and mutant (D) embryos at E13.5. While most TrkA-expressing neurons in NT-3 mutants show normal morphology, there is increase in apoptotic figures associated with TrkA immunoreactivity (arrows). (B,E) RTB immunoreactivity in wild-type (B) and mutant (E) embryos. In E11.5 NT-3 mutant trigeminal ganglion, the number of TrkB-expressing neurons is reduced and the number of apoptosis associated with TrkB immunoreactivity (arrows) is increased. (C,F) RTC immunoreactivity in wild-type (C) and mutant (F) embryos. Numerous TrkC-immunoreactive apoptoses are identified in NT-3 mutant ganglion at E11.5. Scale bar, 20 μm. (G) Quantitation of Trk receptor immunoreactive apoptosis at different embryonic stages in wild type and NT-3 mutants. Note that the numbers for TrkA-, TrkB- and TrkC-immunoreactive apoptosis peaks at E13.5, E11.5 and E11.5, respectively. Counts are derived from at least two animals and are presented as mean ± s.e.m.