Fig. 3.
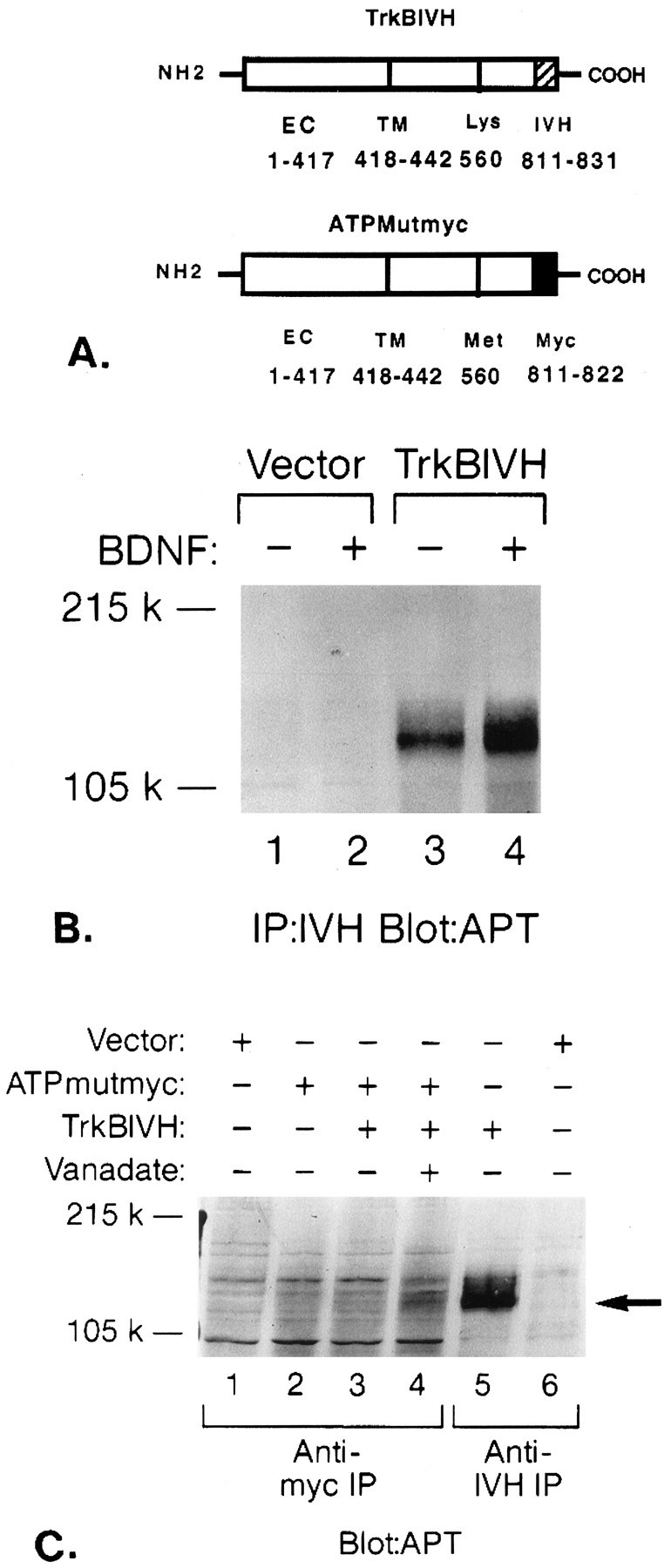
Intermolecular phosphorylation of ATP-binding mutant by wild-type gp145trkB.A, Schematic diagram of epitope-tagged wild-type and mutant trkB receptors. PCR was used to attach an IVH tag to the C terminus of the wild-type trkB receptor (trkBIVH) and myc tag to the C terminus of the ATP-binding mutant (ATPMutmyc) as described in Materials and Methods. Amino acid numbers are listed for the extracellular (EC) or transmembrane domains (TM), ATP-binding site (Lys or Met), and epitope tags (IVH or Myc). B, BDNF induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of trkBIVH receptors. COS cells were transfected with vector control (lanes 1, 2) or trkBIVH (lanes 3, 4). Cells in lanes 2 and 4 were stimulated for 5 min with 100 ng/ml BDNF. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with IVH Ab, separated by 6% SDS-PAGE, and then immunoblotted with the APT Ab 4G10. C, Intermolecular tyrosine phosphorylation of ATPMutmyc by trkBIVH. COS cells were transfected with vector alone (lanes 1, 6), ATPMutmyc (lane 2), ATPmutmyc + trkBIVH (lanes 3, 4), or trkBIVH alone (lane 5). Cells in lane 4 were pretreated with 50 mm sodium orthovanadate for 3 hr before lysis. Cells were stimulated with BDNF, then immunoprecipitated with either anti-myc (lanes 1–4) or anti-IVH Abs (lanes 5, 6). Proteins were separated by 6% SDS-PAGE and were then immunoblotted with APT Ab. The location of gp145trkB is indicated by anarrow.
