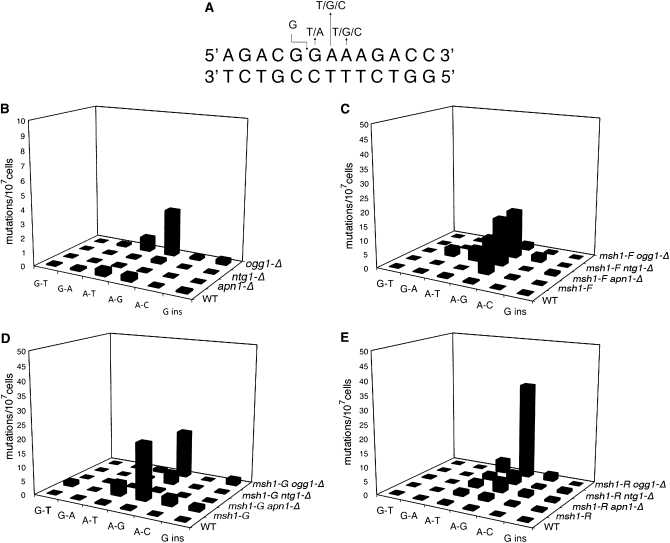
Figure 1.—
(A) The sequence from 1945 to 1957 of the 21S rRNA gene encoded in the mitochondrial genome, the most common site of nucleotide substitutions conferring erythromycin resistance. (B–E) Frequency of base changes in EryR mutant strains. The spectrum of mutations for each strain was determined by sequencing from independent erythromycin-resistant strains, as described in materials and methods. Graphs represent data from 15 to 50 independent colonies for each strain. The frequency of each type of substitution was estimated by multiplying the fraction of each type by the average frequency of EryR for each strain.