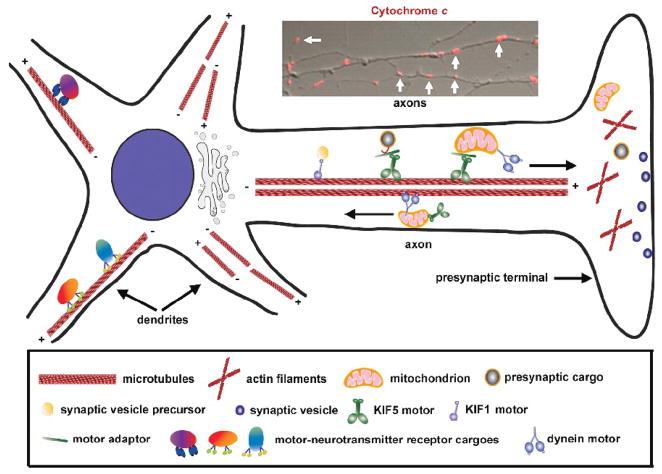
Fig. 1.
Axonal transport of mitochondria from the soma to synapses. In axons, microtubules are uniformly organized with the plus (+) ends facing toward the axonal terminals and the minus (−) ends toward the cell body. However, the organization of microtubules in dendrites shows mixed orientation. Polarity and organization of microtubules in axons are critical for the targeted transport of synaptic cargoes and organelles by microtubule-associated motor proteins. While kinesin motors are mostly plus-end directed, dynein travels toward the minus ends of microtubules. Kinesin KIF5 is the major motor responsible for anterograde transport of axonal mitochondria and dynein drives retrograde axonal transport of mitochondria. Inset: Representative imaging showing Cytochrome c-labeled mitochondria (marked by white arrows) along axonal processes (The image is adapted with permission from Qian Cai, Claudia Gerwin, and Zu-Hang Sheng. Syntabulin-mediated anterograde transport of mitochondria along the neuronal processes. Journal of Cell Biology 170, 959–969. 2005).