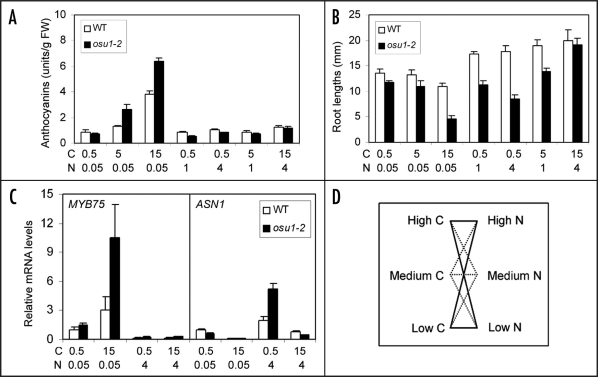
Figure 2.
C/N balance bioassays and gene expression patterns. (A) An example of osu1–2 hypersensitivity to high C/low N in anthocyanin accumulation. (B) An example of osu1–2 hypersensitivity of root growth inhibition in response to high C/low N and low C/high N. (C) Example of gene expression patterns in response to various C/N ratios. Relative mRNA levels of MYB75 and ASN1 genes, using ACTIN2 as an internal control, are shown. WT, wild-type. C (Suc) and N (total N) are in minimolar concentrations. Note that (A–C) were redrawn using the data published elsewhere.24 For more details, please see ref. 24. (D) A proposed mathematical model for C/N balance bioassay and gene expression analysis. Solid lines indicate the four C/N conditions which are recommended the minimum for showing the C/N balance response phenotype, while the dotted lines include other C/N set-ups which will convincingly demonstrate the C/N balance phenotype at various C or N levels or C/N ratios.