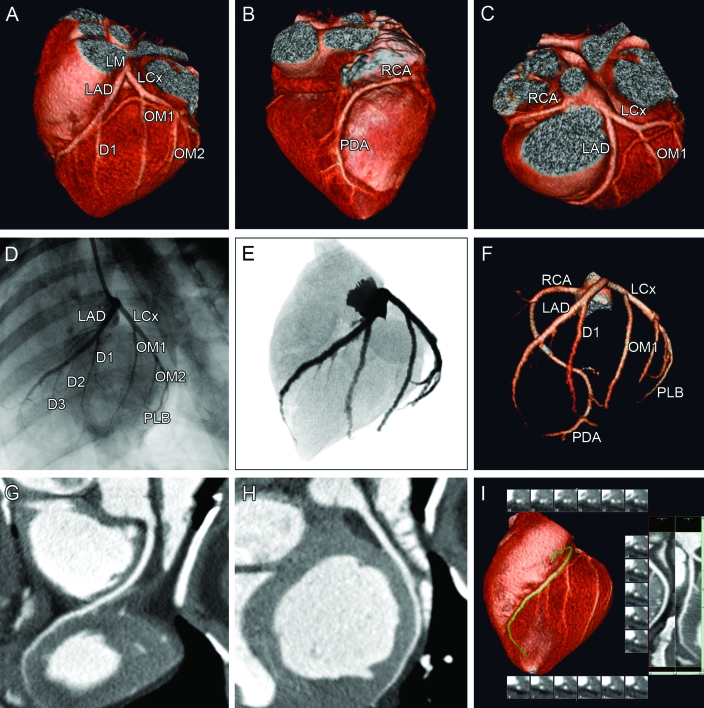
Figure 6.
MDCT images of a normal Göttingen minipig heart and coronary arteries. All images were acquired from the same minipig heart. The upper panel shows the 3D reconstructions. (A) This anteriocranial projection shows the coronary blood supply for the anterior part of the left ventricle. The LAD and the left circumflex coronary artery (LCx) originate from a short left main coronary artery (LM). The LAD first gives off a large diagonal branch (D1). The LCx gives rise to 2 large obtuse marginal branches (OM1 and OM2). (B) In this posterior projection, the right coronary circulation is visualized. The right coronary artery (RCA) descends into the posterior interventricular groove to provide the posterior descending artery (PDA). (C) From the cranial projection the branching of the RCA and the LM dividing into the LAD and LCx can be appreciated. The middle panels show the left coronary vessel system in an anteriolateral projection visualized by (D) conventional coronary angiography and (E) coronarycomputed tomography angiograms eformatted to a conventional angiographic view. (F) Maximum-intensity projection of the coronary tree displays all of the main coronary arteries and the major branches. The bottom panel shows the (G) RCA and (H, I) LAD in a multiplanar reformat, which is used clinically to determine the severity and extent of atherosclerotic plaques.