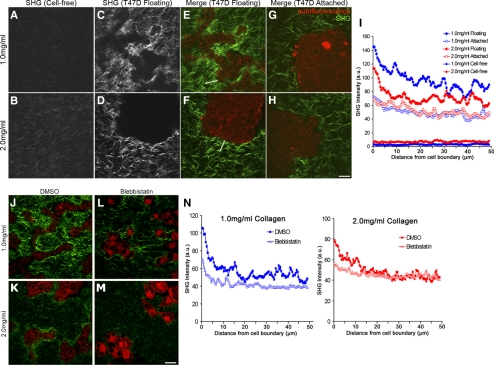
Figure 7.
Establishment of a quantitative assay demonstrates that collagen gel remodeling occurs via contractility. Representative SHG images of low (1.0 mg/ml) and high (2.0 mg/ml) density collagen gels showing random fibril organization of cell-free gels (A and B) compared with floating gels of the same concentration containing cells (C and D). (E–H) MPLSM/SHG merged images of collagen (green) and T47D cell autofluorescence (red) in floating and attached gels of low (1.0 mg/ml) and high (2.0 mg/ml) density. White lines in E and F are examples of a region of interest where SHG fluorescence intensity was measured along line scans and used for data presented in I. Bar, 50 μm. (I) Average SHG fluorescence intensity of collagen fibrils in low and high-density gels. Line scans 50 μm in length were drawn from the edge of the cell–ECM boundary (=0 μm) into the collagen gel and graphed as a function of distance from the edge of the cell. For empty gels, line scans of 50 μm were taken randomly throughout the image. Data represent nine images, three measurements per image, averaged. At 5 μm out from the cell boundary, statistical difference p < 0.001 (1.0 floating vs. 2.0 floating; 2.0 floating vs. 1.0 attached; 2.0 floating vs. 2.0 attached) by the two-sample t test. By regression analysis, p < 0.0001 (1.0 floating vs. 2.0 floating) for each line scan. (J–M) Representative images of collagen (green) and cell autofluorescence (red) show diminished collagen fibril condensation in both low- (1.0 mg/ml) and high (2.0 mg/ml)-density floating collagen gels in the presence of blebbistatin. Bar, 50 μm. (N) Average intensity of collagen fluorescence taken from the edge of the cell–ECM boundary (=0 μm) out 50 μm into the collagen matrix in low- and high-density gels. Data are averaged from a minimum of eight images, three measurements per image. p < 0.01 statistical difference (1.0 DMSO vs. 1.0 blebbistatin), p < 0.05 (2.0 DMSO vs. 2.0 blebbistatin) at 5 μm out by two-sample t test. By regression analysis, p < 0.0001 (1.0 vs. 1.0 + blebbistatin; and 2.0 vs. 2.0 + blebbistatin) for each line scan.