Figure 1. The RNA-Interference Cascade in Humans.
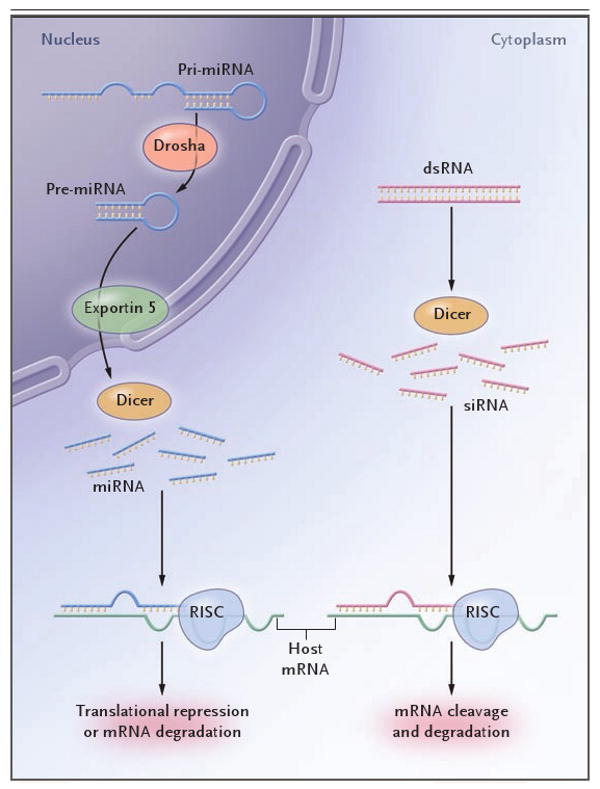
Long precursor microRNA (miRNA) segments, called pri-miRNA, are first cleaved in the nucleus by Drosha, an RNase III endonuclease, into segments of approximately 70 nucleotides each (called pre-miRNA). Transportation into the cytoplasm by means of exportin 5 leads to cleavage by Dicer, another RNase III endonuclease, which produces mature miRNA segments. Host degradation of messenger RNA (mRNA) and translational repression occurs after miRNA binds to the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). Cytoplasmic long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) is cleaved by Dicer into small interfering RNA (siRNA), which is incorporated into RISC, resulting in the cleavage and degradation of specific target mRNA.
