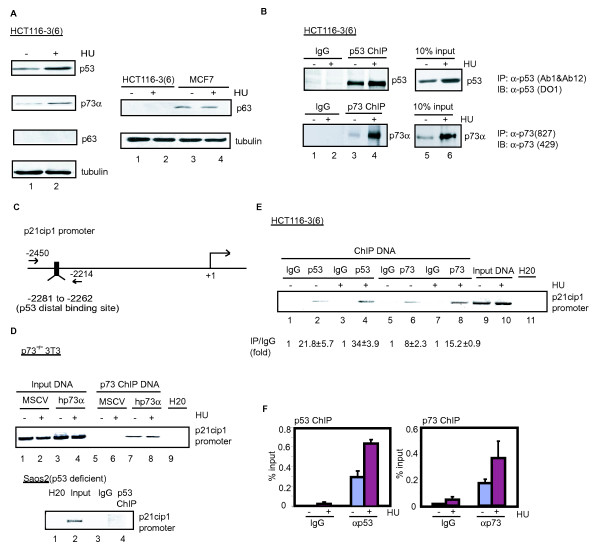
Figure 1.
Hydroxyurea-induced accumulation of p53 and p73 and increased occupancy of the p21cip1 promoter in HCT116-3(6) cells. (a) The indicated cells were treated with or without HU (1 mM) for 16 hours, and the indicated proteins were detected by immunoblotting as described in Methods. (b) Higher levels of p53 and p73 induced by HU correlates with increased association with chromatin. HCT116-3(6) cells with or without HU treatment were subjected to chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) using the indicated antibodies followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (c) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primer designed for the distal p53 binding site in the p21cip1 promoter. (d) ChIP specificity. p73 -/- 3T3 cells reconstituted with either the empty vector or human p73α were treated with or without HU as in (a) and were subjected to ChIP using the indicated antibodies. Enrichment of the p21cip1 promoters was assessed by PCR using primers encompassing the p53-binding site in the distal region of the p21cip1 promoter as shown in (c). (e) Increased occupancy of the p21cip1 promoter by p53 and p73 following HU treatment. Chromatin from HCT116-3(6) cells with or without HU treatment were immunoprecipitated with the indicated antibodies (lanes 2, 4, 6, and 8) and followed by PCR analysis using the primers as shown in (c). M = mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG); R = rabbit IgG. Fold enrichment relative to the IgG sample was determined by quantitative PCR (f) Quantitative real time-PCR analysis of (e) shown as percent total input DNA.