Figure 1.
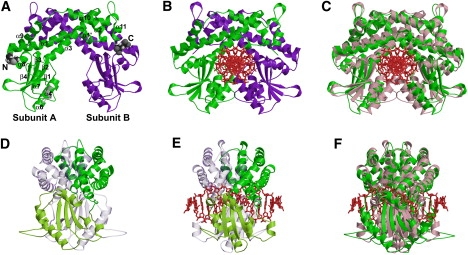
Crystal structures of EcoO109I. (A and B) DNA-free and DNA-bound forms, respectively, colored according to subunits A (green) and B (purple). (A) N-terminal and C-terminal residues are rendered in space-filling. Missing residues in crystal structure were modeled (gray). Secondary structures α1 (residues 2–23), α1′ (residues 26–32), α2 (residues 36–46), α3 (residues 51–75), α4 (residues 91–95), β1 (residues 110–113), β2 (residues 120–128), α6 (residues 133–148), β3 (residues 157–164), α7 (residues 171–178), β4 (residues 194–198), α8 (residues 200–207), α9 (residues 211–227), α10 (residues 236–252), and α11 (residues 262–267) along amino-acid sequence are labeled. (D and E) Side view of DNA-free and DNA-bound forms, respectively, colored according to dimerization (green) and catalytic (pink) domains in one subunit, and counterpart subunit (transparent representation). (C and F) Front and side views of superimposition of DNA-free form (green) and DNA-bound form (pink), respectively.
