Figure 14.
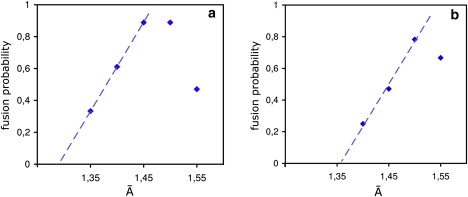
Fusion probability as a function of molecular area for (a) the 14-nm and (b) the 28-nm vesicles. In both cases, the fusion probability, which represents the fraction of fusion attempts that lead to fusion within 20 μs, exhibits a maximum at with 1.45 < < 1.5 in panel a and ≃ 1.5 in panel b corresponding to the tensions ≃ 3.36 and ≃ 4.25, respectively. At higher tensions, fusion becomes less likely because of membrane rupture; at lower tensions, fusion is more and more replaced by adhesion or hemifusion. A linear extrapolation of the data to smaller values of indicates a molecular area threshold for fusion at = 1.29 for the 14-nm and = 1.36 for the 28-nm vesicle. This corresponds to a tension threshold ≃ 0.56 for the 14-nm vesicle and ≃ 1.79 for the 28-nm vesicle.
