Figure 2.
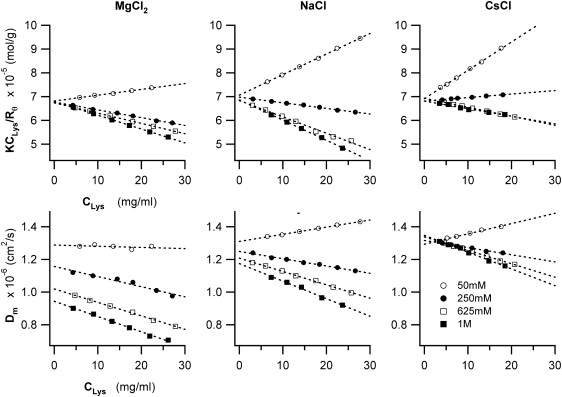
Salt-specific effects on Debye ratios KCLys/R and mutual diffusivities Dm of lysozyme. Plot of (top row) the Debye ratios KCLys/R and (bottom row) mutual diffusivities Dm of lysozyme as function of lysozyme concentration CLys, in the presence of MgCl2, NaCl, or CsCl, at increasing concentrations (○, 50 mM; •, 250 mM; □, 625 mM; and ■, 1 M). The y axis intercepts of the Debye plots yields the inverse of the molecular weight M of lysozyme, whereas the sign of the slope indicates whether interactions among the lysozyme molecules are either net repulsive (positive slope) or attractive (negative slope). For the plots of mutual diffusivities, the y axis intercepts yield the free particle diffusivity D0 at the given solution viscosity, whereas the slope indicates the magnitude and sign of the combined effects of direct and hydrodynamic interactions on mutual lysozyme diffusion. All measurements shown were taken at T = 25°C.
