Figure 2.
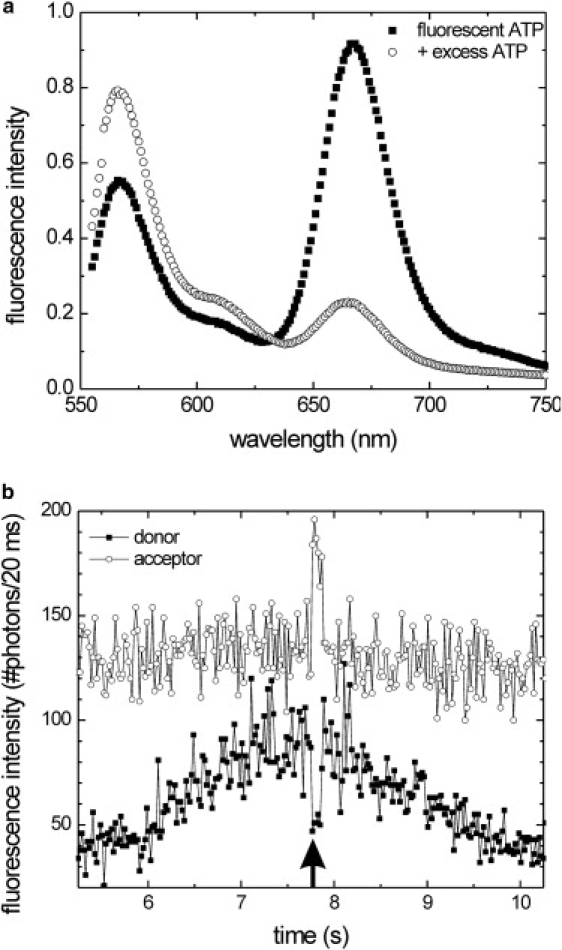
Properties of the fluorescent kinesin-ATP complex. (a) Emission spectra of Alexa Fluor 647-ATP: black squares show the emission spectrum of Alexa Fluor 647-ATP bound to Alexa Fluor 555-labeled kinesin (∼20 nM kinesin with an approximately equimolar amount of fluorescent ATP (see Materials and Methods); λexcitation = 535 nm). The open circles represent the same sample after the addition of 1 mM of regular ATP. The drop of the acceptor emission (∼670 nm) and the rise of the donor emission (∼560 nm) after the ATP chase indicate resonance transfer between Alexa Fluor 647-ATP and Alexa Fluor 555-labeled kinesin. (b) Simultaneously collected fluorescence intensity time traces of both the donor (black squares) and the acceptor channel (open circles) of a donor-labeled kinesin moving through a confocal spot in the presence of 5 μM regular ATP and 0.5 μM fluorescent ATP. A dip in the donor signal (black arrow) is accompanied by a peak in the acceptor intensity, indicating that in this short time interval a fluorescent ATP was bound to the labeled motor domain.
