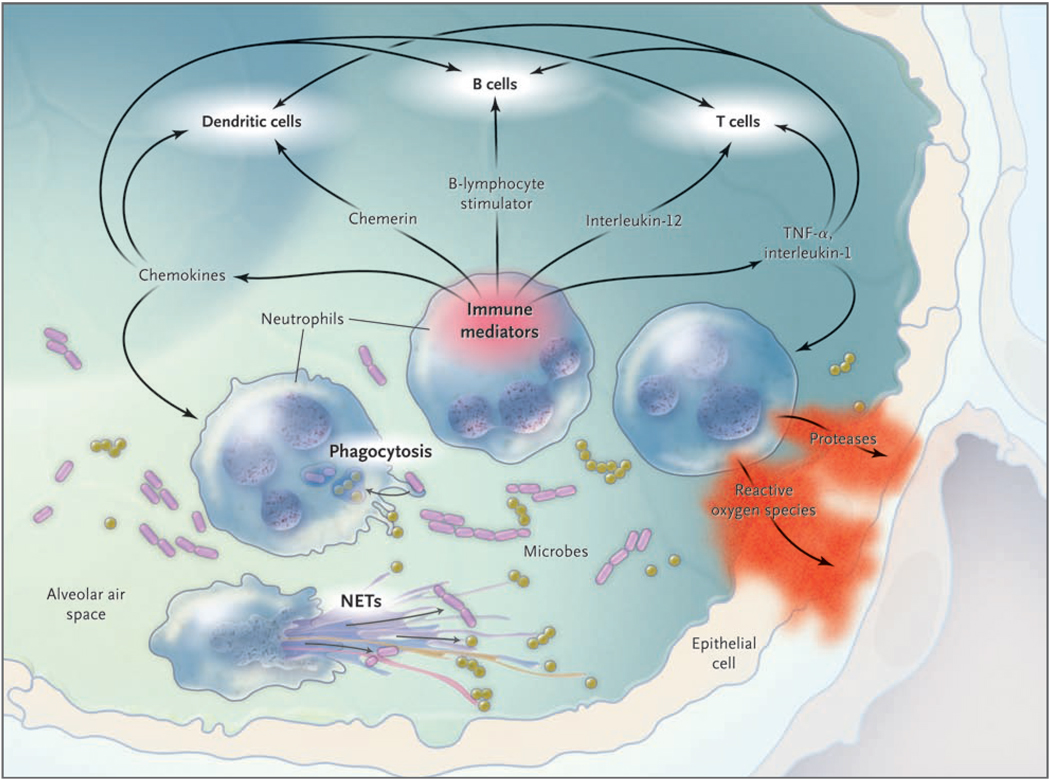
Figure 1. Neutrophils and Lung Infection.
Neutrophils are effector cells of innate immunity, killing microbes using phagocytosis and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). Neutrophils also generate a variety of immune mediators to direct immune responses, influencing other cells of innate and adaptive immunity. Finally, neutrophils damage tissues, with products such as proteases and reactive oxygen species injuring cells and digesting matrix. TNF denotes tumor necrosis factor.