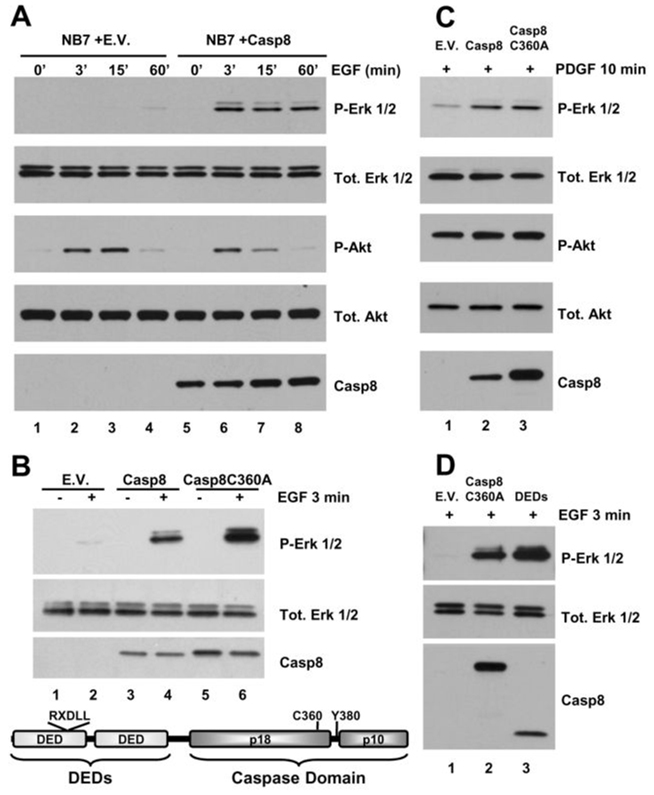
Figure 1. Caspase-8 is essential for EGF-induced activation of the Erk 1/2 pathway.
A) Immunoblot analysis of a time course of EGF (100 ng/mL)-induced Erk and Akt pathway activation in NB7 cells lacking caspase-8 (lanes 1–4) or same re-constituted with wild type protein (lanes 5–8). B) Immunoblot analysis of EGF (100 ng/mL, 3 min)-induced Erk pathway activation in NB7 cells lacking caspase-8 and reconstituted with empty vector (E.V. lanes 1 and 2), or with wild type protein (Casp8, lanes 3 and 4), or an inactivating point mutant of caspase-8 (Casp8C360A, lanes 5 and 6). Schematic depiction of caspase-8 showing domains and residues of interest in this study (below). C) Immunoblot analysis of PDGF (50 ng/mL, 10 min)-induced Erk and Akt pathway activation in NB7 cells lacking caspase-8 re-constituted with empty vector, wild type protein or an inactivating point mutant of caspase-8 (lanes 1–3, respectively). D) Immunoblot analysis of EGF-induced Erk pathway activation in NB7 cells lacking caspase-8 and re-constituted with empty vector, Casp8C360A or with the form of caspase-8 containing DEDs alone (lanes 1–3, respectively).