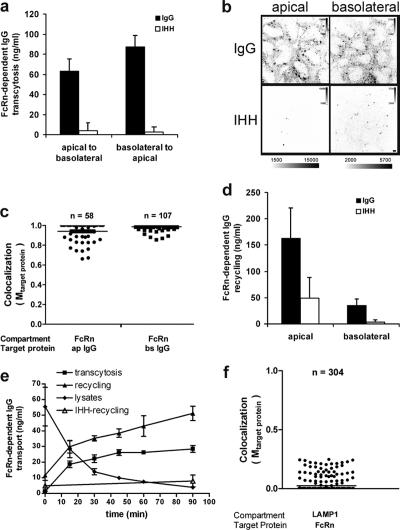
Figure 1.
The fusion protein FcRn-EGFP transports IgG normally in polarized MDCK cells. (a) FcRn-EGFP–mediated transcytosis of NIP-IgG (shaded bars) or mutant NIP-IgG-IHH (open bars) across MDCK cell monolayers measured by NIP-specific ELISA, as described in Materials and methods. Results shown are mean ± SD (n = 4; ANOVA of IgG vs. IHH, P < 0.0002). (b) FcRn-EGFP mediates endocytosis of Alexa Fluor 647–IgG but not Alexa Fluor 647–IgG–IHH from either apical and basolateral surfaces of polarized MDCK cell monolayers, as assessed by confocal microscopy. Intensity scale bars shown demonstrate that images between IgG and IHH were equally contrasted. Bar, 5 µm. (c) IgG is present in FcRn-containing compartments. Cells were incubated with Alexa Fluor 647–IgG as described in panel b and imaged by 3D confocal microscopy. Compartments occupied by both proteins were quantified by first identifying FcRn-EGFP– and IgG-containing objects using an automatic threshold-finding algorithm, and analyzing the colocalization between FcRn-EGFP and IgG using the Manders colocalization coefficient (termed Mtarget protein, see Materials and methods). The distribution of colocalization Mtarget protein for IgG (Target protein) in each FcRn-identified object (Compartment) is shown (data were collected from 40–50 cells of three independent experiments). The horizontal bars indicate a mean Mtarget protein of 0.95 and 0.98 for apically applied IgG (ap IgG) and basolaterally applied IgG (bs IgG), respectively. (d) FcRn-EGFP recycles NIP-IgG (shaded bars) or NIP-IgG-IHH (open bars) after endocytosis from either the apical or basolateral surfaces. In brief, as described in Materials and methods, FcRn-EGFP cell monolayers were incubated with NIP-IgG or the IHH mutant at acidic pH to allow uptake from either cell surface for 1 h. IgG bound at the plasma membrane was removed by washing cells at neutral pH at 4°C. The monolayers were then returned to 37°C and chased for an additional hour in fresh buffer lacking IgG. Results shown are mean ± SD (n = 4, ANOVA for IgG vs. IHH, P < 0.03). (e) Time course of FcRn-EGFP–mediated NIP-IgG basolateral-to-apical transcytosis, recycling, and cell-associated IgG. Individual monolayers were loaded with NIP-IgG or the IHH mutant for 1 h, and surface IgG was stripped at 4°C. The monolayers were then returned to fresh buffer at 37°C and chased for the indicated times to measure recycling (closed triangles), transcytosis (squares), and total IgG cell-associated content (diamonds). Recycling of NIP-IgG-IHH to the basolateral membrane is also shown as control (open triangles). A representative experiment where each point represents the mean of three separate measurements is shown. Error bars indicate the SD of three independent experiments. (f) FcRn is mostly excluded from the lysosomal compartment. Polarized cells were fixed and immunostained for LAMP1. The distribution of colocalization Mtarget protein for FcRn (Target Protein) in each LAMP1-identified object (Compartment) is shown. The horizontal bar indicates mean Mtarget protein = 0.02.