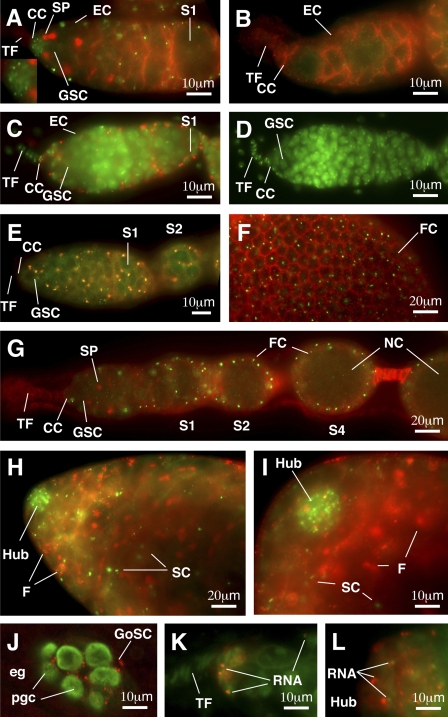
Figure 1.
Yb is localized in discrete spots (Yb bodies) in somatic cells of ovaries and testes. (A–I) Immunofluorescence images of Yb in wild-type and transgenic ovaries (A and C–G) and wild-type testes (H and I), with a null Yb72 mutant ovary (B) shown as a negative control. A and B show a wild-type and a Yb72 germarium, respectively, double stained with a Yb (green) antibody to detect Yb and an adducin antibody (red) to visualize spectrosomes (SP) and fusomes (germline-specific organelles) and to outline somatic cells such as escort cells (EC). The inset in A magnifies cap cells (CC) in this panel. C and D show germaria from w1118 flies containing or lacking a FLAG5-Yb transgene, respectively, double stained for Flag antibody (red) and the DNA dye DAPI (green). E shows a FLAG5-Yb transgenic germarium double stained for Flag (red) and Yb (green). F shows part of an egg chamber double stained for Yb (green) and adducing (red), with focus on the follicle cell (FC) surface. G shows a cross-sectioned image of an ovariole double stained for Yb (green) and adducing (red). H shows the apical end of a wild-type testis double stained for Yb (green) and adducing (red). Yb bodies are enriched in the hub cells and are present in somatic cyst cells (SC) but not in germline cells as marked by fusomes (F). I is a higher magnification of H. (J) An area surrounding the gonad in a germ band retraction stage embryo stained with Yb (red) and Vasa (green) is shown. Yb is localized as spheres and spots in gonadal somatic cells (GoSC) but is not detected in primordial germ cells (pgc; green) in the gonad or in extragonadal somatic cells (eg). K and L show RNA-enriched spots (green) associated with the Yb bodies (red) in the germarium and hub region, respectively. S1, S2, and S4 designate stage 1, 2, and 4 egg chambers, respectively. NC, nurse cell.