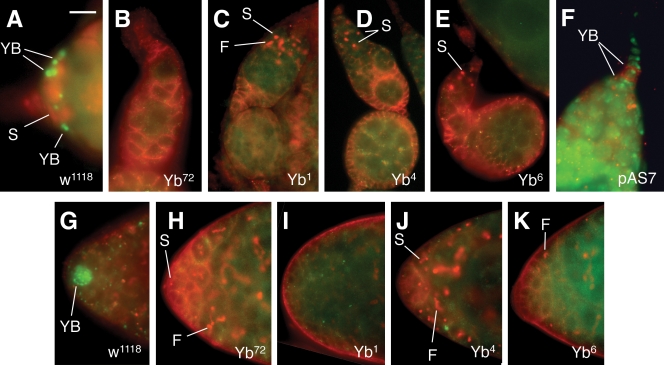
Figure 9.
C-terminal region is required for Yb localization. This figure shows the localization of mutant Yb proteins encoded by five Yb mutant alleles, among which Yb72 is a premature mutation introducing a stop codon at amino acid residue 134 (King et al., 2001) and Yb1, Yb4, and Yb6 are missense mutations that are genetically null (King and Lin, 1999), whereas the pAS7 transgene encodes the C-terminal half of the Yb protein (Fig. 5). (A–E) Wild-type (A) and Yb mutant (B–E) germaria stained for Yb protein (green) and for 1B1 (red) to outline the somatic cells and to label the spectrosome. Yb1, Yb4, and Yb6 mutant proteins are not localized to the Yb body. (F) The localization of the pAS7 mutant Yb protein with the N-terminal half deleted, as detected by anti-His antibody (red) to recognize the Yb body in the wild-type germarium, is shown. The DAPI staining (green) labels the nuclei in the germarium. (G–K) Wild-type (G) and the Yb mutant (H–K) testicular apex stained for Yb protein (green) and for 1B1 (red) to outline the somatic cells and to label the spectrosome. Yb1, Yb4, and Yb6 mutant proteins are not localized to the Yb body in the testis, either. F, fusome; S, spectrosome; YB, Yb body. Bar: (A–F) 10 µm; (G–K) 20 µm.