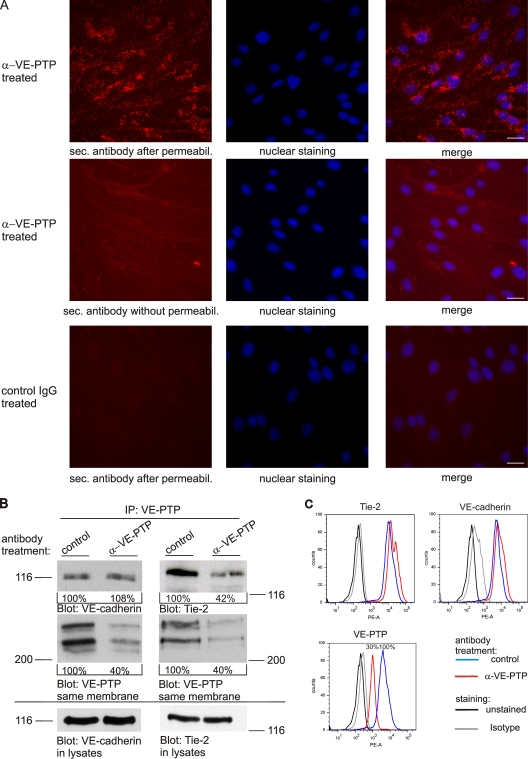
Figure 2.
Antibodies against VE-PTP trigger endocytosis and down-regulation of Tie-2–associated but not VE-cadherin–associated VE-PTP. (A) Confluent bEnd.3 cells were treated with polyclonal antibodies against VE-PTP (α-VE-PTP) or preimmune antibodies (control IgG) for 20 min. Subsequently, cells were either fixed and permeabilized (top and bottom) or only fixed (middle) and stained with Alexa 568–conjugated secondary antibodies. Cell nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst. Bar, 20 µm. (B) bEnd.5 cells were treated with polyclonal antibodies against VE-PTP (α-VE-PTP) or preimmune antibodies (control) for 1 h. VE-PTP was immunoprecipitated from endothelial cells and analyzed by immunoblotting for coprecipitated VE-cadherin and Tie-2, respectively, or for VE-PTP (as indicated underneath). Aliquots of cell lysates with identical protein content were directly immunoblotted for VE-cadherin or Tie-2 (bottom). Quantified signal intensities are indicated. Molecular weight markers are indicated. (C) FACS analysis showing the surface expression of Tie-2, VE-cadherin, and VE-PTP of bEnd.5 cells after 1 h pretreatment with monoclonal antibodies against VE-PTP (red) or preimmune antibodies (blue). The mean fluorescence FACS signal for VE-PTP is indicated in percent (bottom).