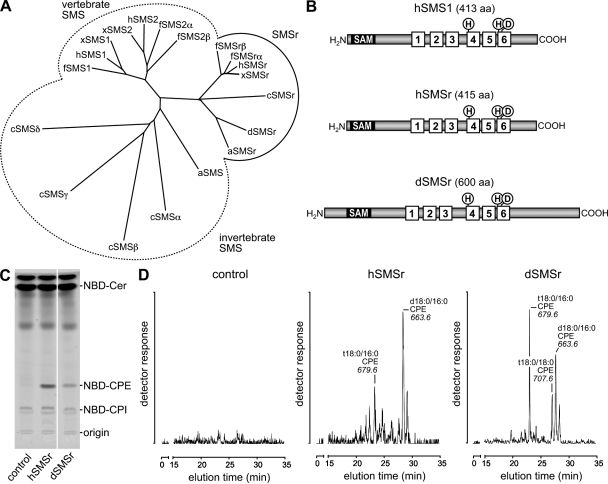
Figure 1.
SMSr proteins display CPES activity. (A) Phylogenetic tree of SMS family members from Homo sapiens (h), Xenopus tropicalis (x), Fugu rubripes (f), Drosophila (d), Apis mellifera (a), and C. elegans (c). The tree was constructed using ClustalX. (B) SMSr proteins share a common domain structure with vertebrate SMS1, which includes six transmembrane helices, an active site consisting of conserved His (H) and Asp (D) residues, and a N-terminal SAM domain. (C) TLC separation of reaction products formed when NBD-Cer was incubated with lysates of yeast strains expressing hSMSr or dSMSr or transfected with empty vector (control). White line indicates that intervening lanes have been spliced out. (D) Yeast strains expressing hSMSr or dSMSr produce CPE in vivo. Different molecular species of CPE were detected by electrospray LC/MS/MS (neutral loss of 141) after alkaline hydrolysis of glycerolipids. No CPE was detected in lipid extracts of control (untransfected) yeast.