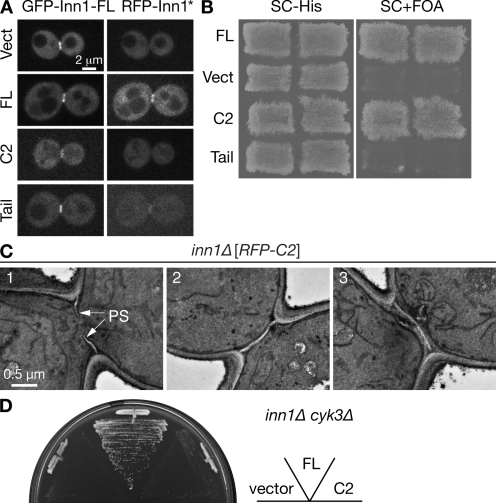
Figure 7.
Structure function analysis of Inn1. (A) Role of the Inn1 C-terminal region in neck localization. Strain LY1310 (inn1Δ [pUG36-INN1]) was transformed with the pUG34mCherry vector (Vect) or its derivatives containing sequences encoding full-length (FL) INN1, the putative C2 domain (amino acids 1–140), or the C-terminal tail (amino acids 130–409). Transformants were incubated on an SC-His-Ura plate for 2 d at 25°C, scraped off, and imaged by spinning-disk confocal microscopy for GFP-Inn1-FL and RFP-Inn1 derivatives (asterisk). (B) Critical role of the putative C2 domain in Inn1 function. The transformants described in A were patched onto SC-His and SC+FOA (to select against pUG36-INN1) plates and incubated at 25°C for 3 d to assess the ability of the INN1 fragments to provide Inn1 function. (C) Restoration of PS formation in inn1Δ cells by the putative C2 domain. Strain YEF5202 (inn1Δ [pUG34mCherry-INN1-C2]), obtained as described in B, was grown to exponential phase in SC-His medium at 24°C and examined by TEM. (D) Cooperative function of Cyk3 and the putative C2 domain of Inn1. Strain MWY1171 (inn1Δ cyk3Δ [pUG36-INN1]) was transformed with the plasmids described in A. The transformants were streaked on an SC-His-Met+FOA plate and incubated for 4 d at 24°C.