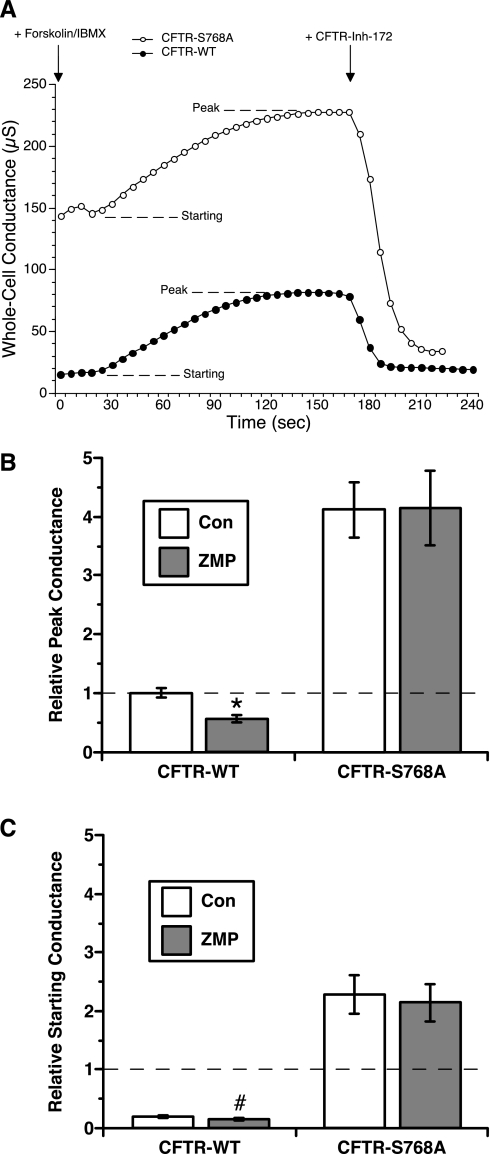
Fig. 5.
Two-electrode voltage-clamp (TEV) measurements of whole cell conductances during PKA agonist stimulation in WT- versus mutant CFTR-expressing Xenopus oocytes with or without AMPK activation. A: representative whole cell conductance recordings from control [potassium gluconate (KG)]-injected oocytes expressing either CFTR-WT or CFTR-S768A. Traces demonstrate the absolute whole cell conductance values measured, the time courses of activation after treatment with 1 μM forskolin + 100 μM IBMX (with starting and peak levels indicated), and the sensitivity to inhibition by treatment at the indicated time with the specific CFTR inhibitor CFTR-Inh-172 (30 μM). B: mean (± SE) peak conductances normalized to the mean control (KG)-injected, CFTR-WT peak conductance for that experimental day and batch in CFTR-WT versus CFTR-S768A-expressing oocytes injected with either control (KG) or AMPK activator [5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleoside monophosphate (ZMP)]. A significant decrease in relative peak conductance was observed for ZMP-injected, CFTR-WT-expressing oocytes (*P < 0.01) but not for ZMP-injected CFTR-S768A-expressing oocytes. C: mean (± SE) starting conductances for the four experimental conditions relative to the mean KG-injected, CFTR-WT peak conductance for that experimental day and batch. CFTR-S768A-expressing oocytes had a dramatically elevated prestimulation starting conductance relative to that of CFTR-WT-expressing oocytes. There was also a ∼40–50% decrease in starting conductance of CFTR-WT-expressing oocytes injected with ZMP versus KG (#P < 0.05), whereas there was no difference in starting conductance between the two conditions for CFTR-S768A-expressing oocytes.