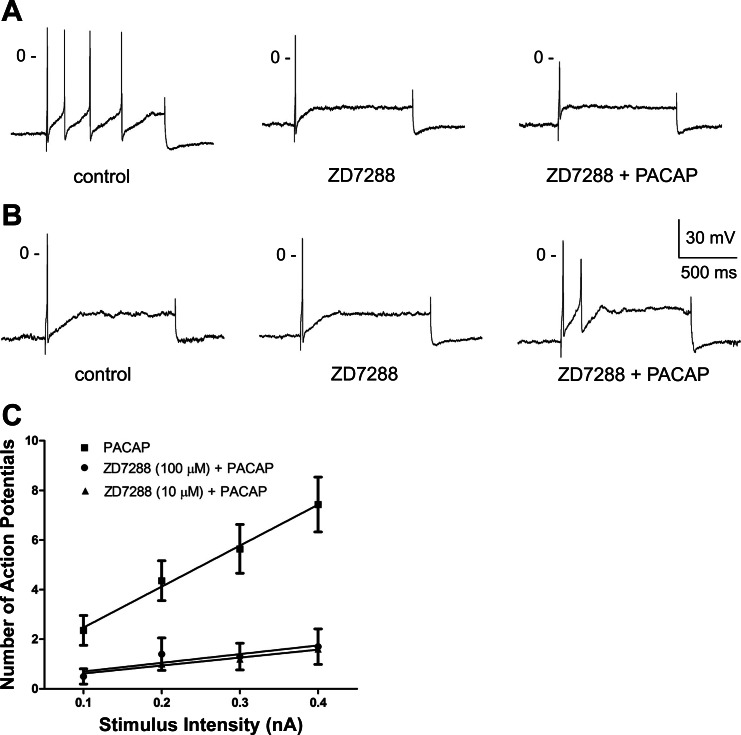
Fig. 2.
ZD7288 suppresses PACAP-induced increase in excitability. A and B: recordings from 2 cells that were initially bathed in control solution, then in a solution containing 100 μM ZD7288, and finally in a solution containing 100 μM ZD7288 + 10 nM PACAP. Exposure to ZD7288 reduced excitability in one cell (A), and PACAP did not increase excitability in either of the ZD7288-treated cells. C: excitability curves summarizing the effect of 10 nM PACAP on excitability for 14 cells kept in control solution, 5 cells bathed in a solution containing 10 μM ZD7288, and 10 cells bathed in a solution containing 100 μM ZD7288. Values are means ± SE of number of action potentials generated by a 1-s depolarizing current pulse at multiple stimulus intensities, with lines fit with a linear regression. Both concentrations of ZD7288 significantly reduced slope of regression line: 16.50 ± 0.92 for PACAP alone, 3.2 ± 0.28 (P < 0.001) for PACAP + 10 μM ZD7288, and 3.5 ± 1.32 (P < 0.001) for PACAP + 100 μM ZD7288.