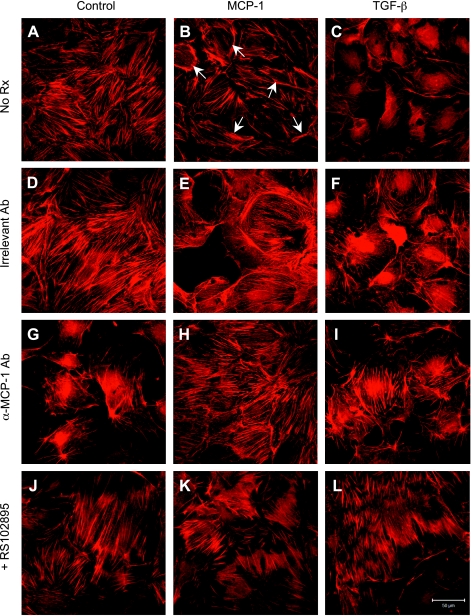
Fig. 6.
MCP-1-induced actin cytoskeleton reorganization in podocytes. A: filamentous (F)-actin strands were visible as cytoplasmic stress fibers in control cells. B: exposure to MCP-1 decreased the density of stress fibers and increased the localization of actin to bundles at the cell periphery (arrows). C: TGF-β-treated cells also showed a loss of stress fibers and increased peripheral actin. D–F: changes in F-actin appearance described above were not affected by an irrelevant hamster IgG, an isotype control. G–I: neutralizing anti-MCP-1 antibody (hamster, 30 μg/ml) greatly reduced the arrangement of F-actin near the cell margins that was secondary to MCP-1 or TGF-β. J–L: RS102895 (6 μM), a specific CCR2 inhibitor, also effectively blocked the MCP-1- or TGF-β-induced actin cytoskeletal reorganization. Magnification: ×400.