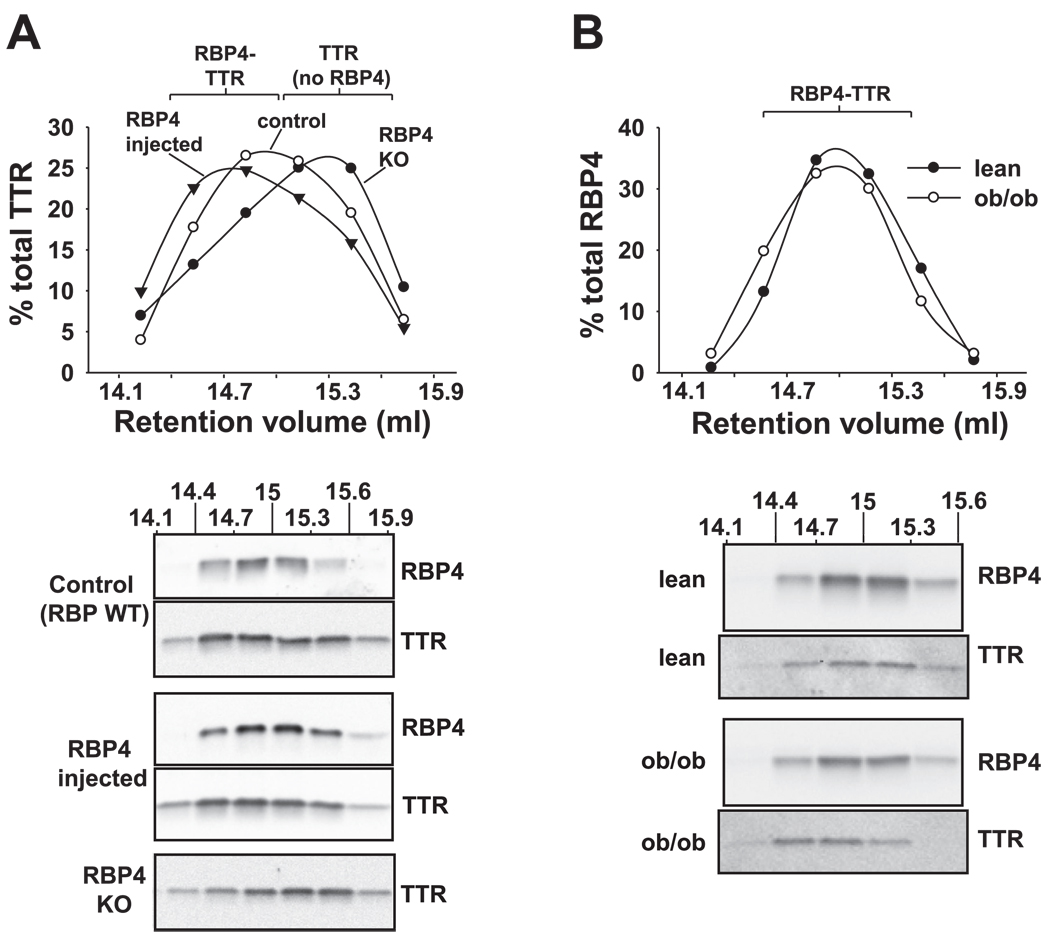
Fig. 3.
Analysis of size distribution of the RBP4-TTR complex by high-resolution gel filtration chromatography. A, top: effects of saturating RBP4 concentrations or absence of RBP4 on the size distribution (eluent fractions 14.1–15.9 ml) of TTR in plasma of normal control mice (○), plasma from normal mice in which RBP4 binding sites on TTR have been saturated by injection of purified RBP4 (▼), and plasma of RBP4-knockout (KO) mice in which no RBP4 is bound to TTR (●). A, bottom: Western blotting of column fractions (14.1–15.9 ml) from mouse plasma with antibodies to RBP4 and/or TTR, corresponding to the size distribution graph above. WT, wild type. Data are representative of 3 mice/genotype. B, top: size distribution of RBP4 in plasma of ob/ob mice (○) or lean littermate control mice (●). The graph shows quantification of bands from Western blotting fractions 14.1–15.6, which contain the RBP4-TTR complex (Fig. 1C). B, bottom: representative Western blots. The volume of ob/ob plasma fractionated was adjusted to approximate the quantity of RBP4 present in lean control plasma. Similar results were obtained in 3 mice of each genotype.