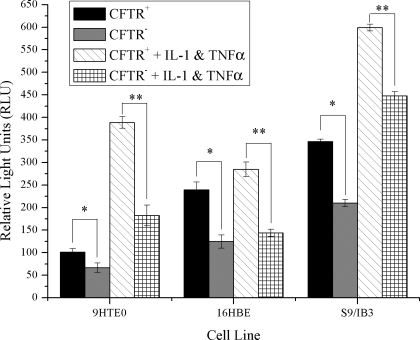
Fig. 1.
There is no elevation in the amount of activated NF-κB in the nucleus of CFTR− cells. NF-κB p65 DNA binding activity was assayed in 9/HTEo cells and human bronchial epithelial (16HBE) cells with and without CFTR function. Cells were placed in serum-free medium 48 h before the preparation of nuclear extract. For inflammatory stimulation, cells were treated with a combination of 1 ng/ml TNFα and 0.5 ng/ml IL-1β for 24 h in serum-free media. A chemiluminescent ELISA-based assay was used to measure active NF-κB p65 transcription factors in 10 μg of nuclear protein. NF-κB p65 DNA binding activity is expressed as relative light units (RLU). Error bars represent SE. n = 6. *P < 0.02 for comparisons of CFTR+ with CFTR− cells for each cell pair. **P < 0.000007 for comparisons of CFTR+ cells treated with TNFα and IL-1β with CFTR− cells treated with TNFα and IL-1β for each cell pair.