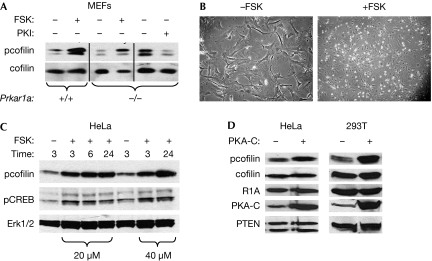
Figure 2.
Activation of PKA causes enhanced pcofilin levels and morphological changes. (A) Immunoblot analysis of pcofilin and cofilin levels in WT (+/+) and knockout (−/−) MEFs treated with forskolin (20 μM) or PKI (5 μM) for 24 h. (B) Morphological and growth pattern changes induced in high-density WT MEFs treated with forskolin for 24 h. Note the similarity to Fig 1A. (C) Time–course analysis of pcofilin and pCREB levels in HeLa cells treated with 20 or 40 μm forskolin. Erk1/2 levels are used as a loading control. (D) Analysis of the levels of pcofilin in HeLa and 293T cells 48 h after transfection with PKA-C shows increased pcofilin without an increase in total cofilin. PTEN was used as a loading control. Erk, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FSK, forskolin; MEF, mouse embryonic fibroblast; PKA, protein kinase A; PKI, PKA inhibitor; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homologue; R1A, Prkar1a; WT, wild type.