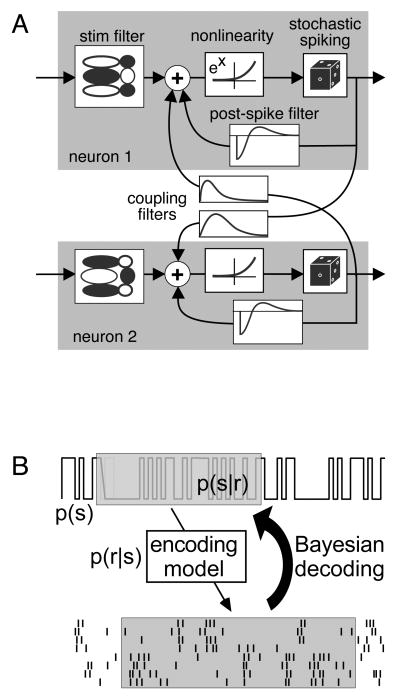
Figure 4.
Decoding the stimulus from population activity [35]. (a) A parametric model (generalized linear model) can capture the activity of a complete population of ON and OFF parasol retinal ganglion cells. Each model neuron spikes stochastically, with a probability equal to the exponentiated summed drive of a linearly filtered stimulus, a post-spike feedback current, and cross-currents from spikes in coupled cells. Because a tractable mathematical expression expresses the likelihood of a population response to any stimulus, P(response|stimulus), one can invert the expression using Bayes rule to optimally reconstruct the stimulus. A model which includes coupling filters captures synchronized firing more accurately, and is able to extract 20% more information about a stimulus, than a model which does not include coupling filters.