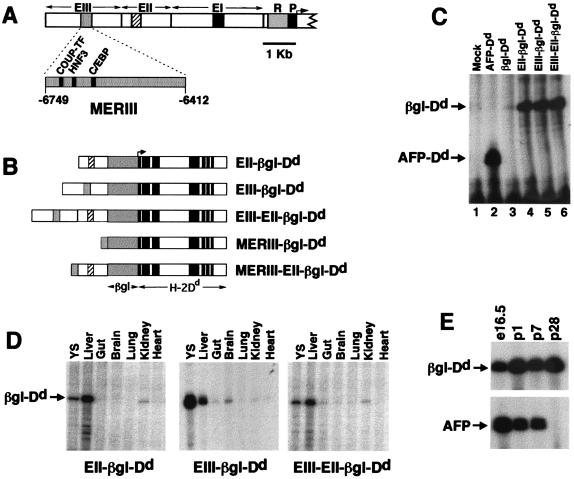
Figure 2.
(A) Map of the AFP regulatory region showing the promoter (P), repressor (R), and enhancers (EI, EII, and EIII). MERI, MERII, and MERIII are shown as black, crosshatched, and stippled boxes, respectively. Expanded view of MERIII shows the relative location of the COUP-TF, HNF3, and C/EBP binding sites. (B) Transgenes used in this study. AFP enhancer regions (EIII, EII, and MERIII) were linked to the human β-globin/H-2Dd reporter gene (βgl-Dd). Transcription initiates from the β-globin promoter and extends through the entire 8-exon Dd gene. (C) Activities of AFP enhancers EII and EIII are equivalent and nonadditive in HepG2 cells. Cells were transfected with the constructs described at the top of the figure. After 48 h, cells were harvested and RNA was prepared. RNase protection assays were performed with a radiolabeled βgl-Dd probe. Transcripts from βgl-Dd constructs protect a 113-nt fragment; transcripts from a control AFP-Dd construct protect a 49-nt fragment. Mock, no DNA. (D) The pattern of transgene activities is similar to AFP in embryonic day 16.5 fetal tissues. RNA was prepared from the tissues described in the figure (YS, yolk sac) and analyzed by RNase protection. Mice containing EII-βgl-Dd, EIII-βgl-Dd, or EIII-EII-βgl-Dd exhibit high levels of transgene mRNA in the liver and yolk sac and low levels in the gut and kidney, similar to the pattern of AFP expression at this time point. The EIII-βgl-Dd transgene also has moderate activity in the fetal brain. (E) EIII-EII-βgl-Dd transgenes continue to be expressed postnatally in the liver. RNA was prepared from the livers of EIII-EII-βgl-Dd mice at embryonic day 16.5 and postnatal days 1, 7, and 28 and used in RNase protection assays with βgl-Dd and AFP probes. The AFP gene is postnatally repressed by 4 wk after birth; transgene mRNA levels do not decline during this period.