Abstract
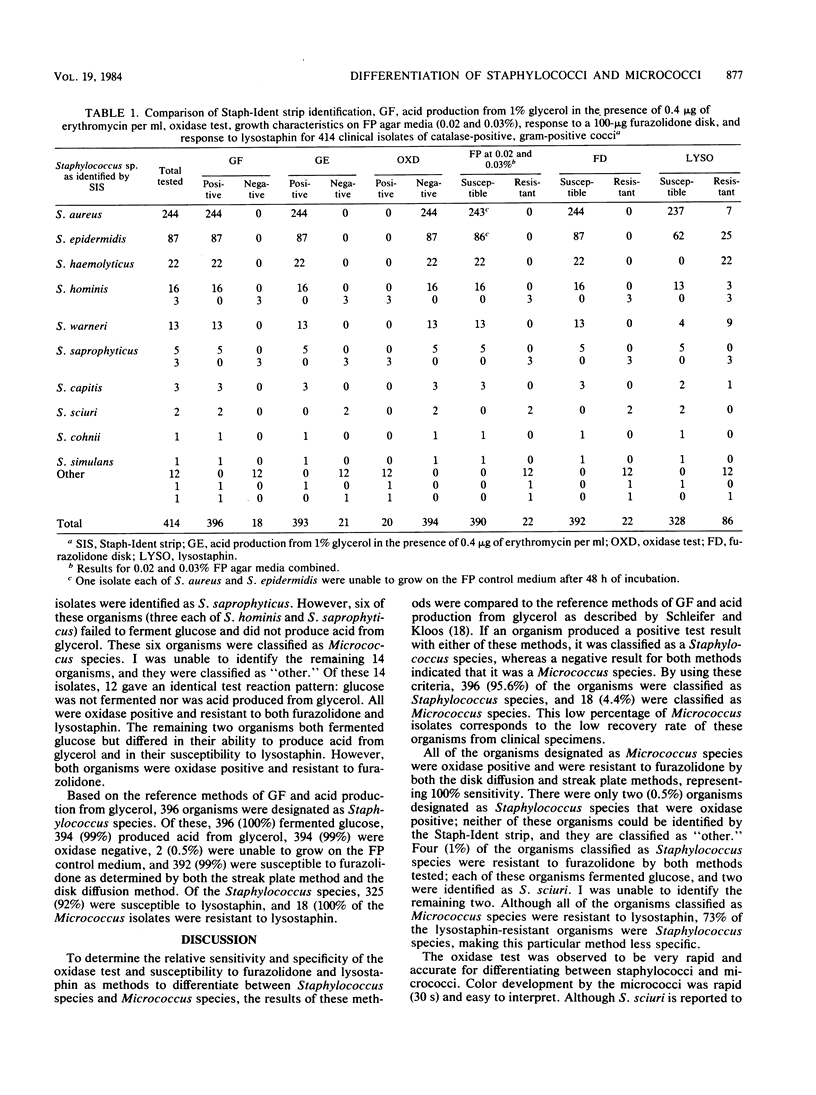
A modified oxidase test (Remel, Lenexa, Kans.) and susceptibility to furazolidone and lysostaphin (Remel) were evaluated in conjunction with the Staph-Ident strip (Analytab Products, Plainview, N.Y.) to accurately differentiate between staphylococci and micrococci. A total of 414 clinical isolates of catalase-positive, gram-positive cocci were each tested with the Staph-Ident strip and by glucose fermentation, acid production from glycerol, susceptibility to furazolidone and lysostaphin, and the oxidase test. Based on the reference methods of glucose fermentation and acid production from glycerol, 396 (95.6%) of the organisms were classified as Staphylococcus species and 18 (4.4%) were classified as Micrococcus species. Of the staphylococci, 99% were oxidase negative and susceptible to furazolidone; 82% were susceptible to lysostaphin. All of the micrococci were oxidase-positive and resistant to furazolidone and lysostaphin. Of the staphylococci, 99% were identified to species by the Staph-Ident strip. However, six (33%) of the micrococci were incorrectly identified as Staphylococcus species (three each of Staphylococcus hominis and Staphylococcus saprophyticus). Because of the demonstrated sensitivity and specificity of the oxidase and furazolidone susceptibility tests, it is suggested that either of these methods be used in the clinical laboratory to accurately differentiate between staphylococci and micrococci. It is also suggested that when working with the Staph-Ident strip, additional testing such as furazolidone susceptibility or oxidase activity should be performed to provide increased accuracy in the differentiation and characterization of members of the family Micrococcaceae.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer G. L. Antimicrobial susceptibility and selection of resistance among Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates recovered from patients with infections of indwelling foreign devices. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):353–359. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWDER H. P., ZYGMUNT W. A., YOUNG J. R., TAVORMINA P. A. LYSOSTAPHIN: ENZYMATIC MODE OF ACTION. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Apr 23;19:383–389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90473-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry J. C., Borovian G. E. Selective medium for distinguishing micrococci from staphylococci in the clinical laboratory. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Nov;4(5):455–457. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.5.455-457.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Digranes A., Oeding P. Characterization of Micrococcaceae from the urinary tract. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Aug;83(4):373–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Smith P. B. The gram positive cocci. Hum Pathol. 1976 Mar;7(2):187–194. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(76)80022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk D., Guering S. J. Differentiation of Staphylococcus and Micrococcus spp. with the Taxo A bacitracin disk. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):719–721. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.719-721.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faller A., Schleifer K. H. Modified oxidase and benzidine tests for separation of staphylococci from micrococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jun;13(6):1031–1035. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.6.1031-1035.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Wolfshohl J. F. Identification of Staphylococcus species with the API STAPH-IDENT system. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):509–516. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.509-516.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Hoeprich P. D., Genigeorgis C. Nuclease production and lysostaphin susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus and other catalase-positive cocci. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):823–826. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.823-826.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liekweg W. G., Jr, Greenfield L. J. Vascular prosthetic infections: collected experience and results of treatment. Surgery. 1977 Mar;81(3):335–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Males B. M., Rogers W. A., Jr, Parisi J. T. Virulence factors of biotypes of Staphylococcus epidermidis from clinical sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Mar;1(3):256–261. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.3.256-261.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsik F. J., Parisi J. T. Significance of Staphylococcus epidermidis in the clinical laboratory. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jan;25(1):11–14. doi: 10.1128/am.25.1.11-14.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskell R. Importance of coagulase-negative staphylococci as pathogens in the urinary tract. Lancet. 1974 Jun 8;1(7867):1155–1158. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90634-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poutrel B., Caffin J. P. Lysostaphin disk test for routine presumptive identification of staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jun;13(6):1023–1025. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.6.1023-1025.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Garner C., Wilcox C., Finland M. Susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis to 65 antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):962–969. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kloos W. E. A simple test system for the separation of staphylococci from micrococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Mar;1(3):337–338. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.3.337-338.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidl P. H., Schleifer K. H. Rapid test for the serological separation of staphylococci from micrococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Mar;35(3):479–482. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.3.479-482.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F. A medium for the study of the ecology of human cutaneous diphtheroids. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Aug;57(3):411–417. doi: 10.1099/00221287-57-3-411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Rheinbaben K. E., Hadlok R. M. Rapid distinction between micrococci and staphylococci with furazolidone agars. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1981 Mar;47(1):41–51. doi: 10.1007/BF00399065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


