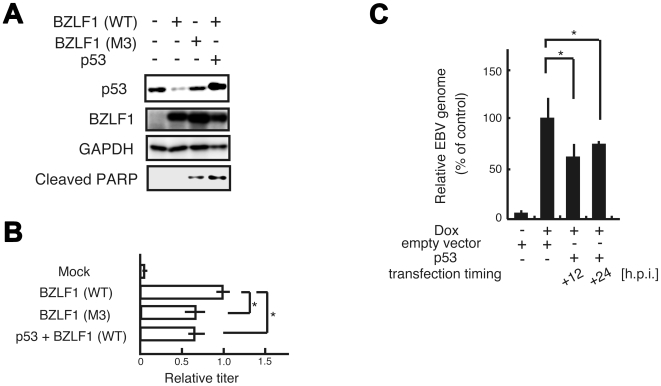
Figure 4. The degradation of p53 during lytic infection is required for efficient viral propagation.
(A) Inhibition of p53 degradation in lytic replication induces apoptosis. The lytic infection was induced by transfection with BZLF1 protein expression plasmid (WT or M3) into 293/EBV cells. Cells were lysed 48 h post-transfection for IB analysis with the indicated antibodies. (B) The expression of p53 reduced the virus yield. The 293/EBV cells were transiently transfected with expression vectors as indicated. The virus yields were determined by counting GFP positive Akata (-) cells. The results are the average of three independent experiments and shown as values relative to the virus yield of BZLF1 (WT) (infectivity value of 1). Asterisk indicates p<0.05. (C) Ectopic expression of p53 at the middle and late stages of lytic infection interferes with efficient viral DNA replication. Tet-BZLF1/B95-8 cells were transfected with p53 expression plasmid using a Microporator at different timings as indicated and then cultured in the presence of doxycycline for 48 h. Viral DNA synthesis was determined by slot blot assay. Asterisk indicates p<0.05.