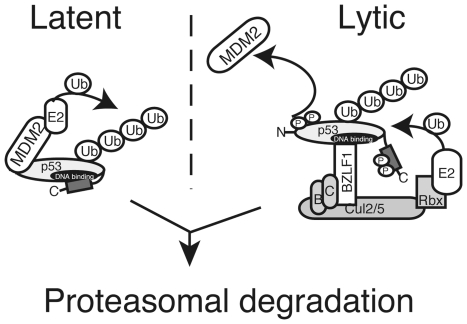
Figure 5. Model for p53 degradation in the EBV life cycle.
With EBV latent infection, the level of p53 is regulated by MDM2 E3 ubiquitin ligase. Induction of lytic replication elicits the DNA damage response via activation of the ATM-dependent DNA damage signaling pathway. Under these conditions, p53 is hyperphosphorylated at S15 by ATM and S20, S366 and S378 by Chk2. C-terminal phosphorylation of p53 leads to allosteric conformational change through dissociation of the negative regulatory domain (gray) from the DNA binding domain (black), enhancing the binding of BZLF1 protein to p53. BZLF1 protein associated ECS ubiquitin ligase complexes then ubiquitinate p53, leading to proteasomal degradation during lytic infection.