Figure 2.
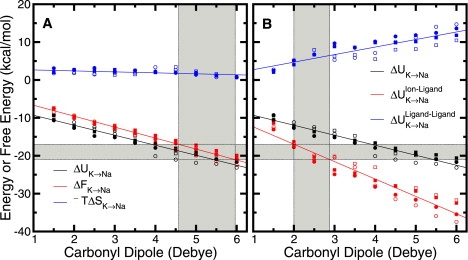
Thermodynamic breakdown for K+ → Na+ in naive 8-ligand toy models as a function of the dipole moment of the carbonyl-like ligands. Shown are results from calculations using standard (circles) and modified (squares, Table S2) CHARMM parameters for a range of assigned dipole moment, where the absolute value of partial charge on C or O is ≲ e. The calculations used either a half-harmonic (solid shapes) or a LJ (open shapes) restraint (see Methods). The gray shaded area along the ordinate axes demarcates a liberal range of values for the difference in K+ and Na+ hydration free energy. The lower and upper bounds of this range were taken from a combination of experiment (28) and model calculations (24). (A) Total internal energy, ΔU, and entropic, −TΔS, contributions to the net free energy, ΔF, for the alchemical reaction as a function of the dipole moment assigned to the fictitious ligands. The shaded gray region along the abscissa indicates a range of dipole moment for which ΔF is roughly equal to the difference in K+ and Na+ hydration free energy. (B) Ion-ligand and ligand-ligand interaction contributions to the net total internal energy as a function of the dipole moment assigned to the fictitious ligands. The shaded gray region along the abscissa indicates a range of dipole moment for which the energy from ion-ligand interactions is roughly equal to the difference in K+ and Na+ hydration free energy.
