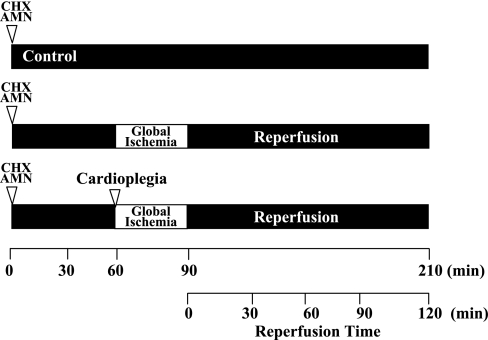
Fig. 1.
Experimental protocol. All experiments consisted of 60 min of equilibrium followed by 30 min of global ischemia (GI) and 120 min of reperfusion. Control hearts were perfused without GI at 37°C for 210 min. GI hearts were subjected to 30 min of GI and 120 min of reperfusion. Cardioplegia (CP) hearts received magnesium-supplemented potassium CP solution containing diazoxide (50 μM) for 5 min before GI and 120 min of reperfusion. To determine the role of RNA or protein synthesis in the cardioprotection afforded by CP, a separate group of control and CP hearts was preperfused for 55 min with Krebs-Ringer solution containing either α-amanitin (AMN; 2.5 μg/ml) to inhibit RNA synthesis or cycloheximide (CHX; 50 μg/ml) to inhibit protein synthesis. Control + AMN and control + CHX hearts were then perfused for a further 155 min. CP + AMN and CP + CHX hearts received CP for 5 min before 30 min of GI and 120 min of reperfusion.