Figure 1.
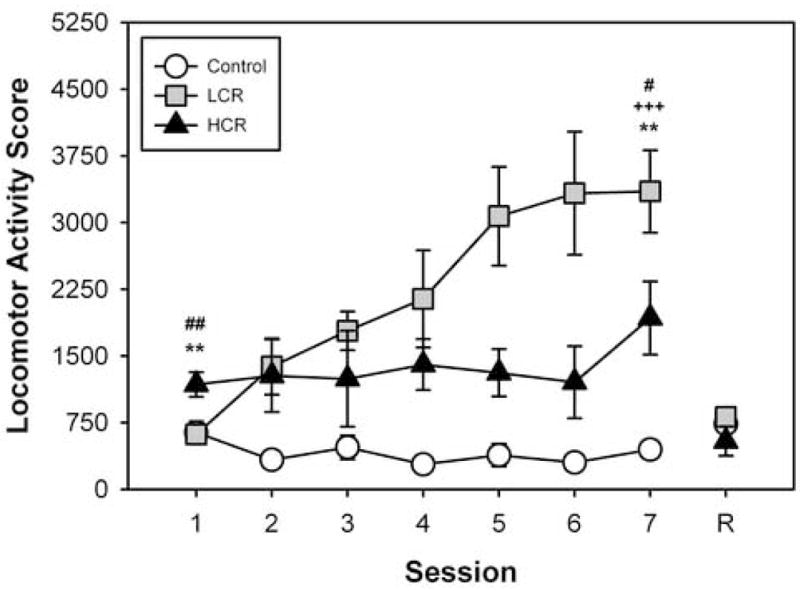
Repeated i.p. cocaine injections induce locomotor sensitization in LCRs, but not in HCRs, when locomotor activity is measured in a CPP apparatus. Vehicle or cocaine (10 mg/kg, i.p.) was administered once daily for seven days to the control and experimental groups, respectively. Ordinate: Locomotor Activity Score, representing consecutive beam breaks in the CPP apparatus during the 30-min post-injection interval. Abscissa: Session. On day 8 for a reversal test (R), rats in the control group (n=4) were given cocaine whereas LCRs (n=6) and HCRs (n=6) were given vehicle. Mean values ± SEM. +++, p < 0.001, control vs. LCR; #, p < 0.05, control vs. HCR; ##, p < 0.01, control vs. HCR; ** p<0.01, LCR vs. HCR. Although significant between group differences were revealed by ANOVA at sessions one, four, five, six and seven, only post-hoc comparisons at sessions one and seven are presented on the figure.
